摘要
我们致力于解决机器翻译质量的准确评估问题,同时努力将翻译精度提升至人工翻译水平。本研究采用5个不同的基准翻译模型,通过3种评估指标对其性能进行衡量,并结合先前研究的成果不断优化模型精度。
目录
- 引言
- 数据集
- 机器翻译精度评估方法
- 3.1. BLEU 分数
- 3.2. BLEURT 分数
- 3.3. COMET 分数
- 五个基准机器翻译模型及其精度
- 4.1. Azure 基线模型
- 4.2. Azure 自定义模型
- 4.3. DeepL 模型
- 4.4. Google 翻译
- 4.5. GPT-4 模型
- 4.6. 对比与结论
- 提升机器翻译精度
- 5.1. GPT-4 的上下文学习
- 5.2. 混合模型
- 5.3. GPT-4 作为数据清洗工具
- 结论
- 参考文献
1. 引言
随着 AI 技术的进步,特别是 OpenAI 推出 ChatGPT 之后,人们对 AI 行业的信任度不断提升。作为自然语言处理领域的核心技术,机器翻译正变得愈发重要。
本文重点评估了5个基础翻译模型的性能,采用多种评估指标进行对比,同时深入探讨了尽可能提升模型精度的方法。
2. 数据集
本研究使用 Hugging Face 上的 Opus100(ZH-EN)数据集。该数据集包含100万条跨领域的中英翻译实例,是训练翻译模型的理想选择。

注意: 必须指出,数据集中存在翻译错误。虽然这些错误看似会降低训练精度,但同时也有助于防止过拟合问题。
此外,在将数据集整合到 Azure AI 平台之前,需要进行预处理以去除每个句子中的异常符号。
3. 机器翻译精度评估方法
面对众多翻译模型,选择最适合特定用途的模型颇具挑战性。评估翻译模型主要有两种基本方法:
- 传统方法:BLEU 分数
- 神经网络指标:BLEURT 分数和 COMET 分数
3.1 BLEU 分数
BLEU(Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)是一种用于评估机器翻译文本质量的算法(Papineni et al., 2002)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import nltk
bleu_scores = []
for reference, pre in zip(reference_translations, prediction):
reference_tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(reference.lower())
pre_tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(pre.lower())
if not reference_tokens or not pre_tokens:
continue
bleu_score = nltk.translate.bleu_score.sentence_bleu(
[reference_tokens], pre_tokens,
smoothing_function=nltk.translate.bleu_score.SmoothingFunction().method2)
bleu_scores.append(bleu_score)
average_bleu_score = sum(bleu_scores) / len(bleu_scores)
print("Average BLEU score:", average_bleu_score)
|
七种平滑函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|
| Smoothing Function 1 | 加法(拉普拉斯)平滑 - 添加常数值防止零概率 |
| Smoothing Function 2 | NIST 平滑 - 引入参考句长度惩罚 |
| Smoothing Function 3 | Chen and Cherry - 根据候选译文长度自适应调整 |
| Smoothing Function 4 | JenLin - 平衡加法方法和调整方法 |
| Smoothing Function 5 | Gao and He - 修正对短译文的偏差 |
| Smoothing Function 6 | 贝叶斯方法 - 为长句提供稳健估计 |
| Smoothing Function 7 | 几何均值 - 计算 n-gram 精度的几何平均值 |
注意: BLEU 存在局限性:它无法考量词序和句法结构,主要依赖 n-gram 重叠,无法反映流畅度、习惯用语、语法和整体连贯性。
3.2 BLEURT 分数
BLEURT 是一种自然语言生成评估指标,输入参考句和候选句对,返回表示流畅度和语义保留程度的分数(Sellam, 2021)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from bleurt import score
checkpoint = "/path/to/BLEURT-20"
scorer = score.BleurtScorer(checkpoint)
scores = scorer.score(references=reference_translations, candidates=prediction)
total_score = sum(scores) / len(scores)
print("Total Score:", total_score)
|
提示: 使用 BLEURT 前需要先安装 TensorFlow。
3.3 COMET 分数
COMET 是一个用于训练多语言机器翻译评估模型的神经网络框架,旨在预测人类对翻译质量的判断。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from comet import download_model, load_from_checkpoint
model_path = download_model("Unbabel/wmt22-comet-da")
model = load_from_checkpoint(model_path)
data = []
for src, pre, reference in zip(source_sentences, preds, reference_translations):
data.append({
"src": src,
"mt": pre,
"ref": reference
})
model_output = model.predict(data, batch_size=8, gpus=0)
print(model_output)
|
4. 五个基准机器翻译模型及其精度
4.1 Azure 基线模型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import requests, uuid, json
endpoint = ""
subscription_key = ""
location = ""
path = '/translate'
constructed_url = endpoint + path
params = {
'api-version': '3.0',
'from': 'zh',
'to': 'en'
}
headers = {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': subscription_key,
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region': location,
'Content-type': 'application/json',
'X-ClientTraceId': str(uuid.uuid4())
}
body = []
for i in source_sentences:
body.append({'text': i})
request = requests.post(constructed_url, params=params, headers=headers, json=body)
response = request.json()
|
4.2 Azure 自定义模型
Azure 自定义模型是利用额外数据集对 Azure 基线模型进行进一步训练后的增强版本。自定义模型在 Azure 平台上的 BLEU 分数为 39.45。
注意: 使用自定义模型时,必须先在 Azure 平台上发布,才能通过 API 调用。
4.3 DeepL 模型
DeepL 翻译是一种使用卷积神经网络和英语枢轴的神经机器翻译服务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import deepl
API_KEY = 'your-api-key'
source_lang = 'ZH'
target_lang = 'EN-US'
translator = deepl.Translator(API_KEY)
results = translator.translate_text(source_sentences, source_lang=source_lang, target_lang=target_lang)
|
4.4 Google 翻译
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import requests
def translate_texts(texts, target_language):
api_key = 'your-api-key'
url = 'https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2'
translations = []
for text in texts:
params = {
'key': api_key,
'q': text,
'target': target_language
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
translated_text = data['data']['translations'][0]['translatedText']
translations.append(translated_text)
return translations
|
4.5 GPT-4 模型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import openai
def translate_text(text_list):
openai.api_key = 'your-api-key'
translations = []
for text in text_list:
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a translation assistant from Chinese to English. Some rules to remember:\n\n- Do not add extra blank lines.\n- It is important to maintain the accuracy of the contents, but we don't want the output to read like it's been translated. So instead of translating word by word, prioritize naturalness and ease of communication."},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=messages,
max_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
timeout=30
)
choices = response['choices']
if len(choices) > 0:
translation = choices[0]['message']['content']
translations.append(translation)
return translations
|
注意: 与其他4个模型相比,GPT-4 的响应速度较慢。此外,过多的 token 可能导致过载。
4.6 对比与结论
基于评估结果:
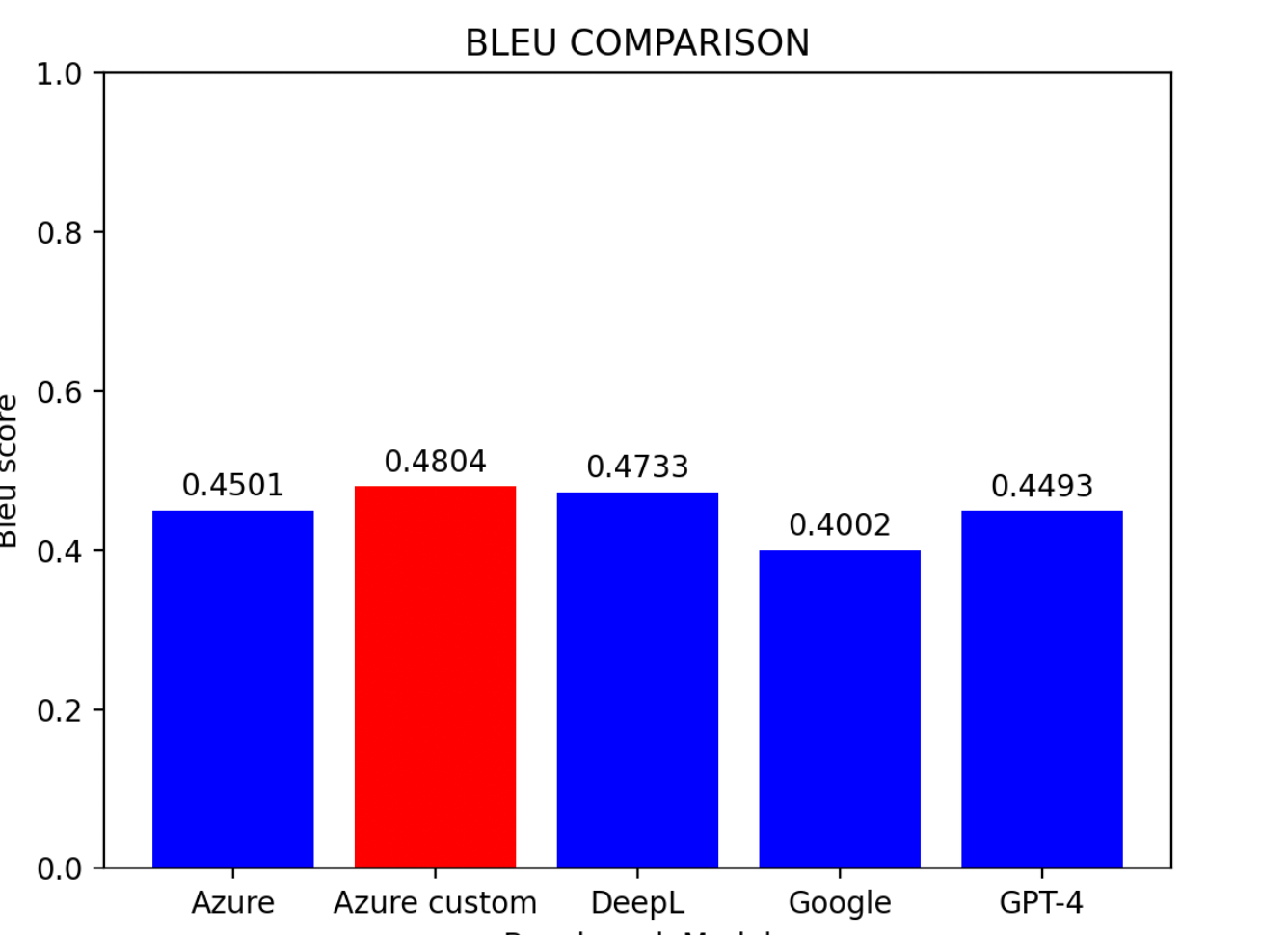
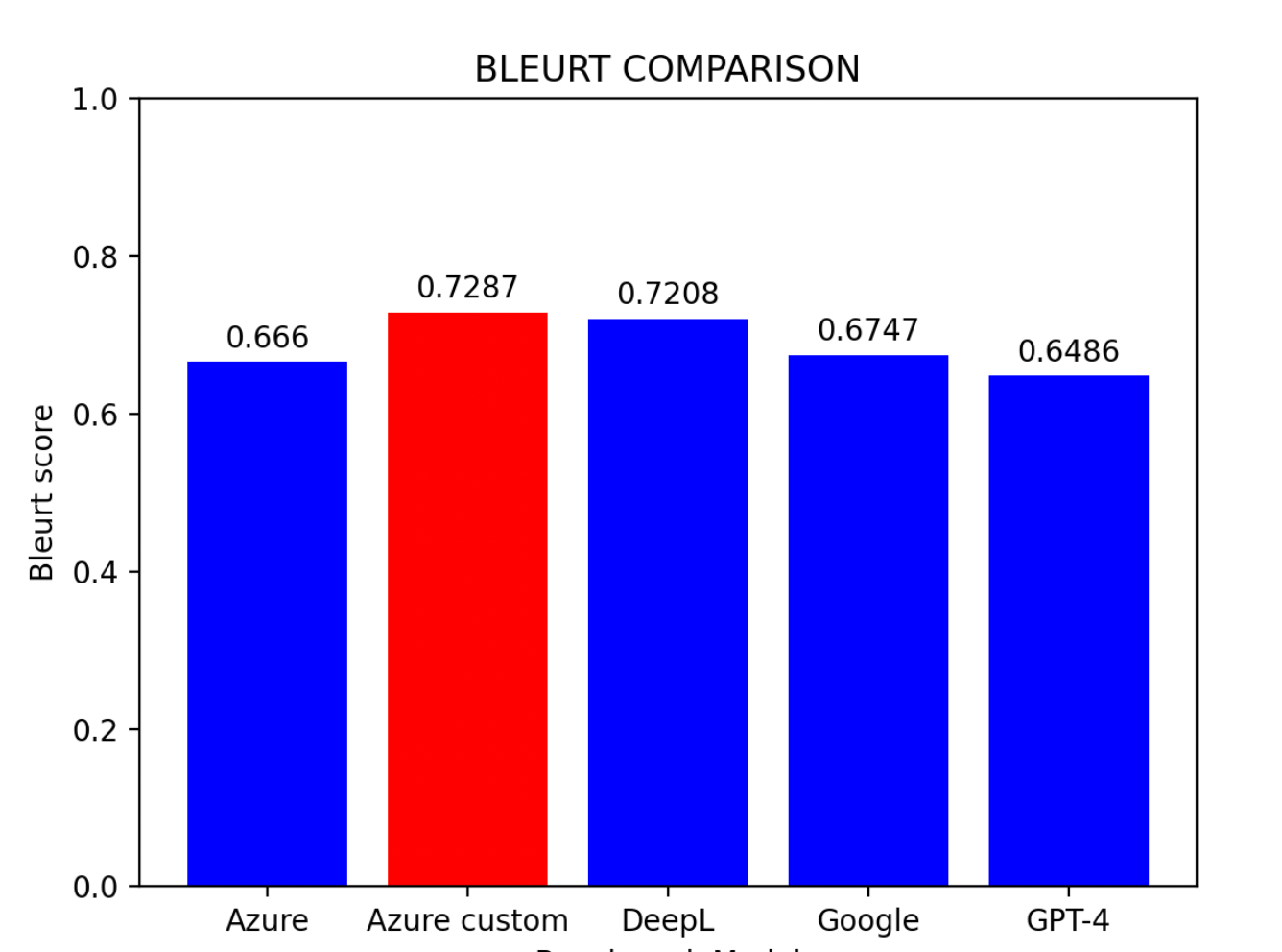
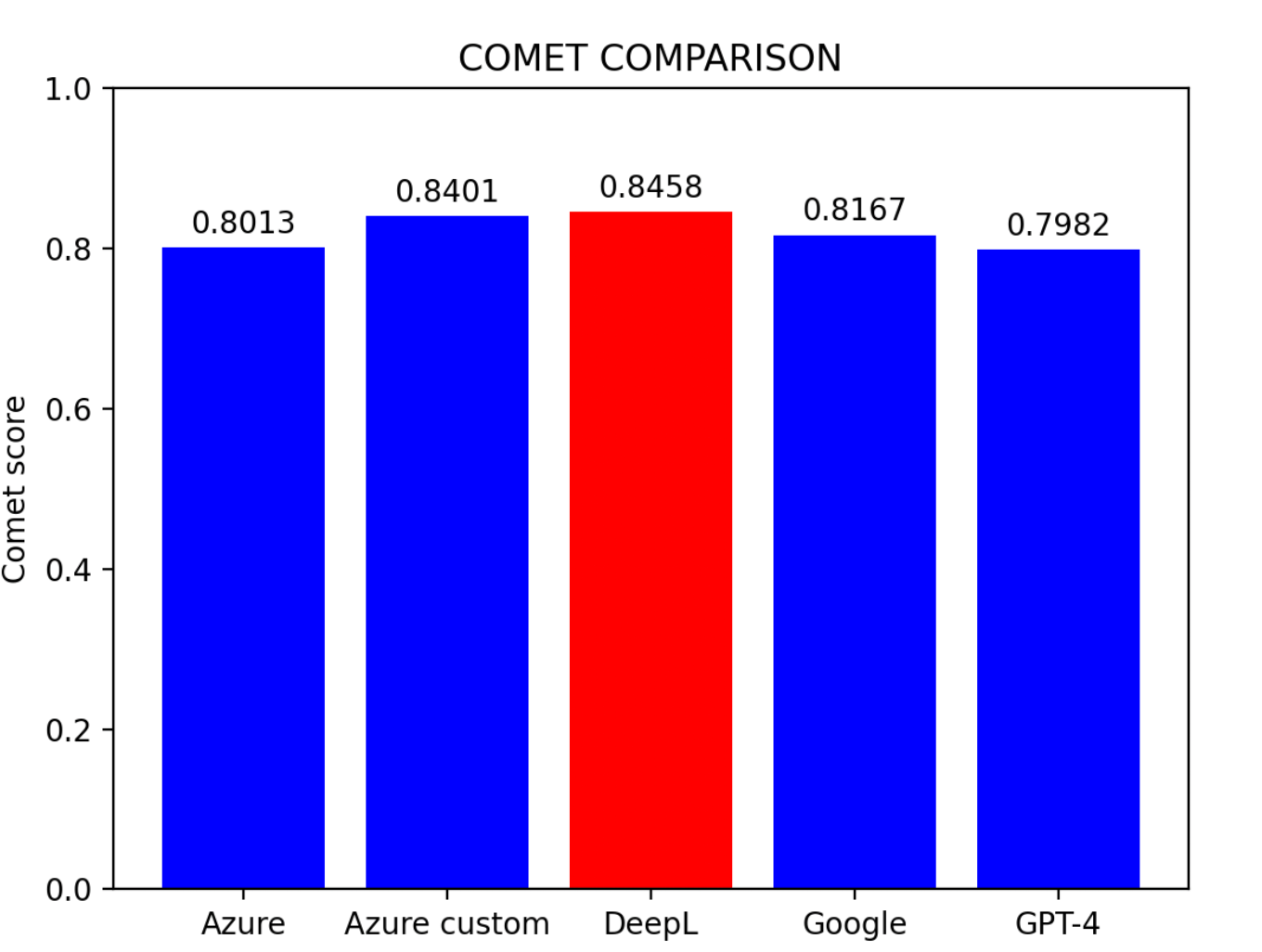
主要发现:
- Azure 自定义模型表现最优
- DeepL 紧随其后,位列第二
- Azure 基线模型位居第三
- Google 翻译和 GPT-4 水平相当
提示: 对于没有预训练条件的用户,DeepL 是目前中译英翻译中最有效的模型。
5. 提升机器翻译精度
我们探讨了三种不同的翻译精度提升方法。
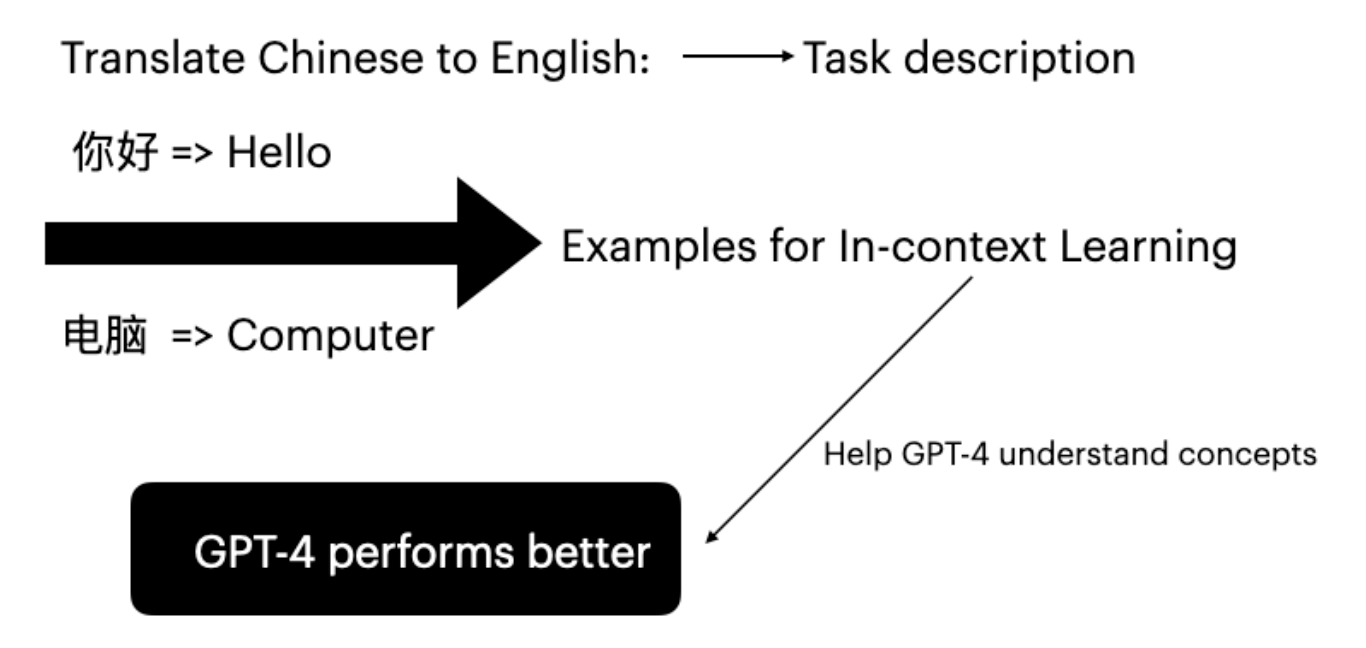
5.1 GPT-4 的上下文学习
大语言模型可以通过在提示词中提供特定任务示例的上下文学习来提升性能(Brown et al., 2020)。
结果: BLEURT 分数从 0.6486 提升至 0.6755,验证了上下文学习的有效性。
5.2 混合模型
混合阈值模型设定特定阈值,当某些句子未达到阈值时,使用不同的模型进行重新翻译。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import requests, uuid, json
import openai
from comet import download_model, load_from_checkpoint
def translate_with_fallback(text):
translation_from_Azure = Azure_translation(text)
model_path = download_model("Unbabel/wmt22-comet-da")
model = load_from_checkpoint(model_path)
refined_translation = []
indices_to_correct = []
for i in range(len(translation_from_Azure)):
data = [{
"src": source_sentences[i],
"mt": translation_from_Azure[i],
"ref": reference_translations[i]
}]
res = model.predict(data, batch_size=1, gpus=0)
if res.scores[0] < 0.81:
indices_to_correct.append(i)
sentences_to_correct = [source_sentences[i] for i in indices_to_correct]
corrected_sentences = gpt_translation(sentences_to_correct)
corrected_index = 0
for i in range(len(translation_from_Azure)):
if i in indices_to_correct:
refined_translation.append(corrected_sentences[corrected_index])
corrected_index += 1
else:
refined_translation.append(translation_from_Azure[i])
return refined_translation
|
混合模型的结论
- 最佳阈值与 COMET 分数一致
- Azure 自定义 + DeepL 或 DeepL + GPT-4 组合效果最佳
- 几乎所有混合模型都优于单一模型
- 提高阈值并不一定能带来更高的分数
5.3 GPT-4 作为数据清洗工具
GPT-4 可用于预处理数据集并修正不准确的翻译:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import openai
import json
pair = {}
for zh, en in zip(source_sentences, reference_translations):
pair[zh] = en
def translate_text(pair):
openai.api_key = 'your-api-key'
translations = []
for zh, en in pair.items():
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Chinese to English translation corrector. You need to modify the incorrect English translations below and correct it by given Chinese sentences, please remember not to use English abbreviations and not add extra blank lines. Fix weird punctuation. And the result should be English sentences only"},
{"role": "user", "content": json.dumps({"zh": zh, "en": en})}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=messages,
max_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
timeout=30
)
choices = response['choices']
if len(choices) > 0:
model_response = choices[0]['message']['content']
translations.append(model_response)
return translations
|
提示: 利用 GPT-4 对原文和译文同时进行数据清洗是行之有效的方法。在经过精炼的数据集上,Azure 基线模型的得分可以达到 DeepL 在未清洗数据集上的表现水平。
6. 结论
本文通过3种评估指标和5个基准模型,对机器翻译精度及其改进方法进行了系统研究。
核心结论:
- DeepL 是最出色的中译英翻译工具
- Azure 基线模型在拥有充足数据和适当训练的条件下可以达到更高性能
- 结合不同翻译引擎的混合模型可以提升翻译精度
- GPT-4 数据清洗能有效提升数据集质量,进而改善模型表现
注意: 本研究存在一定局限性:人工检查发现部分获得高分的翻译实际质量并不理想,且部分精度改进方法反而导致分数下降。
7. 参考文献
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W. J. (2002). BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL).
Thibault Sellam (2021). BLEURT
Tom Brown et al. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners.
Daniel Bashir (2023). In-Context Learning, in Context. The Gradient.
Amr Hendy et al. (2023). How Good Are GPT Models at Machine Translation? A Comprehensive Evaluation. Microsoft.
Ricardo Rei (2022). COMET