摘要
在通信技术快速发展的背景下,以 OpenAI Whisper 模型为代表的最新突破显著提升了多语言语音转文字的准确性和可及性。然而,在识别精度方面仍有提升空间。本研究专注于越南语和日语的自动语音识别(ASR)模型性能优化。
我们采用标准指标进行评估:越南语使用词错误率(WER),日语使用字符错误率(CER)。
核心结果:
- 越南语(FOSD + Common Voice + Google Fleurs + Vivos):WER 9.46%
- 日语(ReazonSpeech + Common Voice + Google Fleurs):CER 8.15%
目录
- 背景介绍
- 环境搭建
- 数据集加载
- 数据预处理
- 训练
- 参数高效微调
- 结果
- 评估
- Azure Speech Studio
- 总结
1. 背景介绍
在当今社会,通信与技术已不可或缺,但在可及性、包容性和高效知识传播方面仍面临诸多挑战。自动语音识别(ASR)技术的进步正在简化人机交互,尤其体现在在线会议场景中。
ASR 是将语音信号转换为对应文本的过程。近年来,随着大规模语音数据集及其转录文本的可用性提高,各大企业纷纷关注这一领域。

OpenAI Whisper 是一个基于 Transformer 的编码器-解码器模型,采用 sequence-to-sequence 架构设计。它以音频频谱图特征作为输入,将其转换为文本 token 序列。具体过程如下:
- 特征提取器将原始音频转换为 log-Mel 频谱图
- Transformer 编码器生成编码器隐藏状态序列
- 解码器通过 cross-attention 机制预测文本 token
2. 环境搭建
Whisper 微调有两种方式:使用 Google Colab,或在本地 PC 上运行代码。
所需依赖包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| python -m pip install -U pip
pip install evaluate pandas numpy huggingface_hub pydub tqdm spacy ginza audiomentations
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
pip install datasets>=2.6.1
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
pip install librosa
pip install evaluate>=0.30
pip install jiwer
pip install gradio
pip install -q bitsandbytes datasets accelerate loralib
pip install -q git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@main git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git@main
|
注意: 本文微调实验使用的硬件配置为 Windows 11 Pro、AMD Ryzen 7 3700X 8核处理器、80GB 内存、GeForce RTX 3090 显卡。
3. 数据集加载
方法一:通过 Hugging Face 加载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from datasets import load_dataset, DatasetDict
common_voice = DatasetDict()
common_voice["train"] = load_dataset(
"mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0", "ja",
split="train+validation", use_auth_token=True
)
common_voice["test"] = load_dataset(
"mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0", "ja",
split="test", use_auth_token=True
)
common_voice = common_voice.remove_columns([
"accent", "age", "client_id", "down_votes",
"gender", "locale", "path", "segment", "up_votes"
])
|
方法二:手动准备数据集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import os, csv, codecs
def text_change_csv(input_path, output_path):
file_csv = os.path.splitext(output_path)[0] + ".csv"
output_dir = os.path.dirname(input_path)
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, file_csv)
encodings = ["utf-8", "latin-1"]
for encoding in encodings:
try:
with open(input_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as rf:
with codecs.open(output_file, 'w', encoding=encoding, errors='replace') as wf:
readfile = rf.readlines()
for read_text in readfile:
read_text = read_text.split('|')
writer = csv.writer(wf, delimiter=',')
writer.writerow(read_text)
print(f"CSV has been created using encoding: {encoding}")
return True
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
|
使用的数据集
| 数据集 | 语言 | 获取方式 | 语音时长 |
|---|
| Common Voice 13.0 | 越南语、日语 | Hugging Face | 19小时(VN)、10小时(JP) |
| Google Fleurs | 越南语、日语 | Hugging Face | 11小时(VN)、8小时(JP) |
| Vivos | 越南语 | Hugging Face | 15小时 |
| FPT Open Speech Dataset | 越南语 | 下载并解压 | 30小时 |
| VLSP2020 | 越南语 | 下载并解压 | 100小时 |
| ReazonSpeech | 日语 | Hugging Face | 5小时 |
| JSUT | 日语 | 下载并解压 | 10小时 |
| JVS | 日语 | 下载并解压 | 30小时 |
4. 数据预处理
数据增强
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| from audiomentations import Compose, AddGaussianNoise, TimeStretch, PitchShift
common_voice = common_voice.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16000))
augment_waveform = Compose([
AddGaussianNoise(min_amplitude=0.005, max_amplitude=0.015, p=0.2),
TimeStretch(min_rate=0.8, max_rate=1.25, p=0.2, leave_length_unchanged=False),
PitchShift(min_semitones=-4, max_semitones=4, p=0.2)
])
def augment_dataset(batch):
audio = batch["audio"]["array"]
augmented_audio = augment_waveform(samples=audio, sample_rate=16000)
batch["audio"]["array"] = augmented_audio
return batch
common_voice['train'] = common_voice['train'].map(augment_dataset, keep_in_memory=True)
|
转录文本归一化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import string
def remove_punctuation(sentence):
translator = str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation)
modified_sentence = sentence.translate(translator)
return modified_sentence
def fix_sentence(sentence):
transcription = sentence
if transcription.startswith('"') and transcription.endswith('"'):
transcription = transcription[1:-1]
transcription = remove_punctuation(transcription)
transcription = transcription.lower()
return transcription
|
准备 Whisper 输入数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| def prepare_dataset(batch):
audio = batch["audio"]
batch["input_features"] = processor.feature_extractor(
audio["array"], sampling_rate=audio["sampling_rate"]
).input_features[0]
batch["input_length"] = len(audio["array"]) / audio["sampling_rate"]
transcription = fix_sentence(batch["transcription"])
batch["labels"] = processor.tokenizer(
transcription, max_length=225, truncation=True
).input_ids
return batch
common_voice = common_voice.map(
prepare_dataset,
remove_columns=common_voice.column_names['train'],
num_proc=1,
keep_in_memory=True
)
|
5. 训练
Data Collator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import torch
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Union
@dataclass
class DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding:
processor: Any
def __call__(self, features: List[Dict[str, Union[List[int], torch.Tensor]]]) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
input_features = [{"input_features": feature["input_features"]} for feature in features]
batch = self.processor.feature_extractor.pad(input_features, return_tensors="pt")
label_features = [{"input_ids": feature["labels"]} for feature in features]
labels_batch = self.processor.tokenizer.pad(label_features, return_tensors="pt")
labels = labels_batch["input_ids"].masked_fill(labels_batch.attention_mask.ne(1), -100)
if (labels[:, 0] == self.processor.tokenizer.bos_token_id).all().cpu().item():
labels = labels[:, 1:]
batch["labels"] = labels
return batch
data_collator = DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding(processor=processor)
|
评估指标(越南语 - WER)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import evaluate
metric = evaluate.load("wer")
def compute_metrics(pred):
pred_ids = pred.predictions
label_ids = pred.label_ids
label_ids[label_ids == -100] = tokenizer.pad_token_id
pred_str = tokenizer.batch_decode(pred_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
label_str = tokenizer.batch_decode(label_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=pred_str, references=label_str)
return {"wer": wer}
|
评估指标(日语 - CER)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import spacy, ginza
nlp = spacy.load("ja_ginza")
ginza.set_split_mode(nlp, "C")
def compute_metrics(pred):
pred_ids = pred.predictions
label_ids = pred.label_ids
label_ids[label_ids == -100] = processor.tokenizer.pad_token_id
pred_str = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(pred_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
label_str = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(label_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# 对日语文本进行分词后评估
pred_str = [" ".join([str(i) for i in nlp(j)]) for j in pred_str]
label_str = [" ".join([str(i) for i in nlp(j)]) for j in label_str]
wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=pred_str, references=label_str)
return {"wer": wer}
|
训练参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| from transformers import Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
model.config.dropout = 0.05
training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
output_dir="./whisper-fine-tuned",
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
gradient_accumulation_steps=1,
learning_rate=1e-6,
lr_scheduler_type='linear',
optim="adamw_bnb_8bit",
warmup_steps=200,
num_train_epochs=5,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
fp16=True,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
predict_with_generate=True,
generation_max_length=255,
eval_steps=500,
logging_steps=500,
report_to=["tensorboard"],
load_best_model_at_end=True,
metric_for_best_model="wer",
greater_is_better=False,
push_to_hub=False,
save_total_limit=1
)
|
提示: 关键训练参数说明:
- learning_rate:1e-5 或 1e-6 效果最佳
- warmup_steps:建议设置为总步数的 10%
- per_device_train_batch_size:根据 GPU 显存设置(RTX 3090 可设为 16)
- dropout:设为 0.05 或 0.10 以防止过拟合
6. 参数高效微调(PEFT)
PEFT 仅使用**全部参数的 1%**进行训练,即可达到与全量微调相当的性能。
| 全量微调 | 参数高效微调 |
|---|
| 训练速度较快 | 训练时间较长 |
| 需要大量计算资源 | 计算资源消耗少 |
| 重新训练整个模型 | 仅修改少量参数 |
| 容易过拟合 | 不易过拟合 |
LoRA 配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| from transformers import WhisperForConditionalGeneration, prepare_model_for_int8_training
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path, load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto"
)
model = prepare_model_for_int8_training(model)
def make_inputs_require_grad(module, input, output):
output.requires_grad_(True)
model.model.encoder.conv1.register_forward_hook(make_inputs_require_grad)
config = LoraConfig(
r=32,
lora_alpha=64,
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none"
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# Output: trainable params: 15728640 || all params: 1559033600 || trainable%: 1.01%
|
7. 结果
越南语结果
在 FOSD + Google Fleurs + Vivos + CV 数据集上微调的模型取得了最低 WER 9.46%。
日语结果
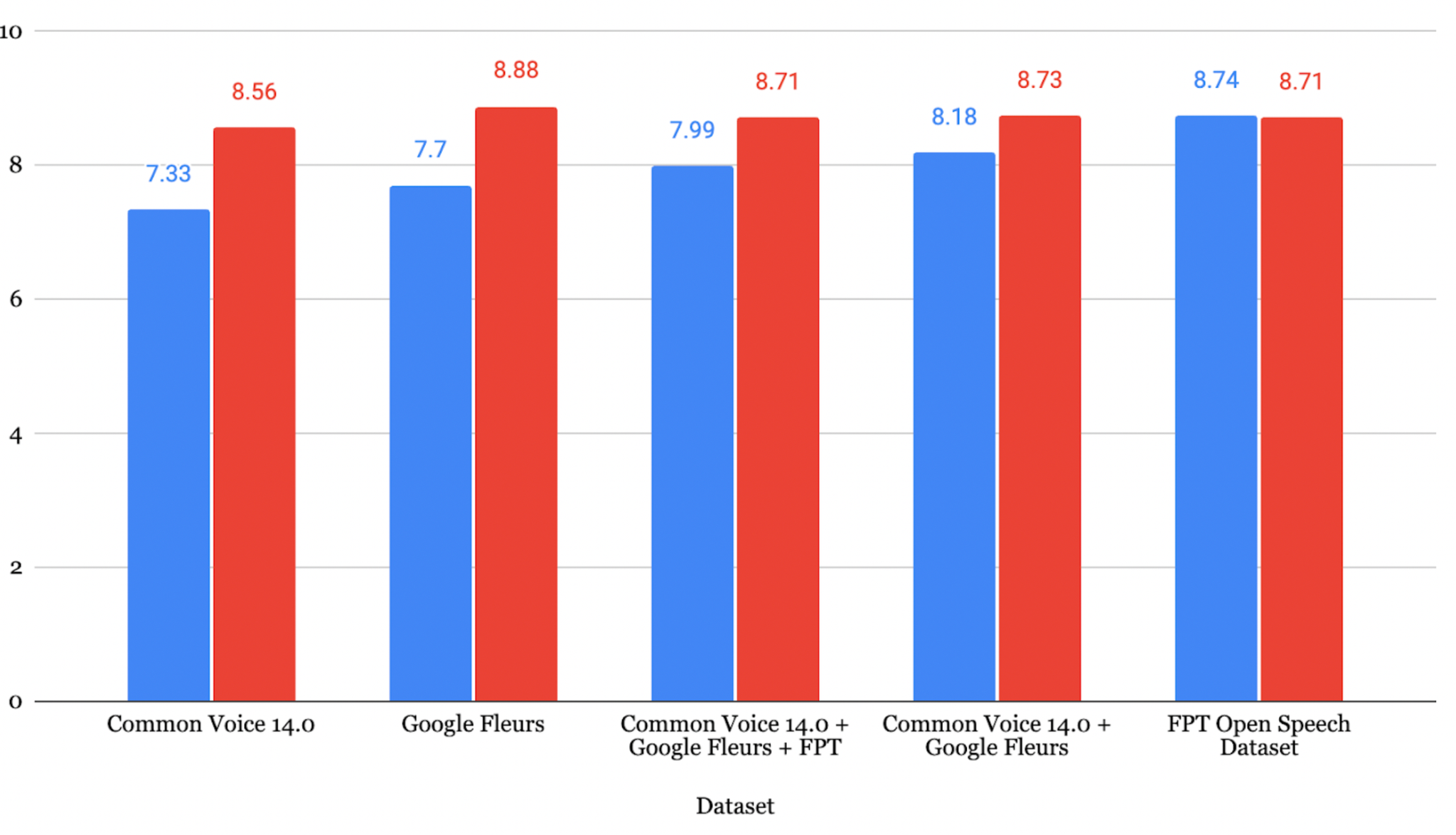
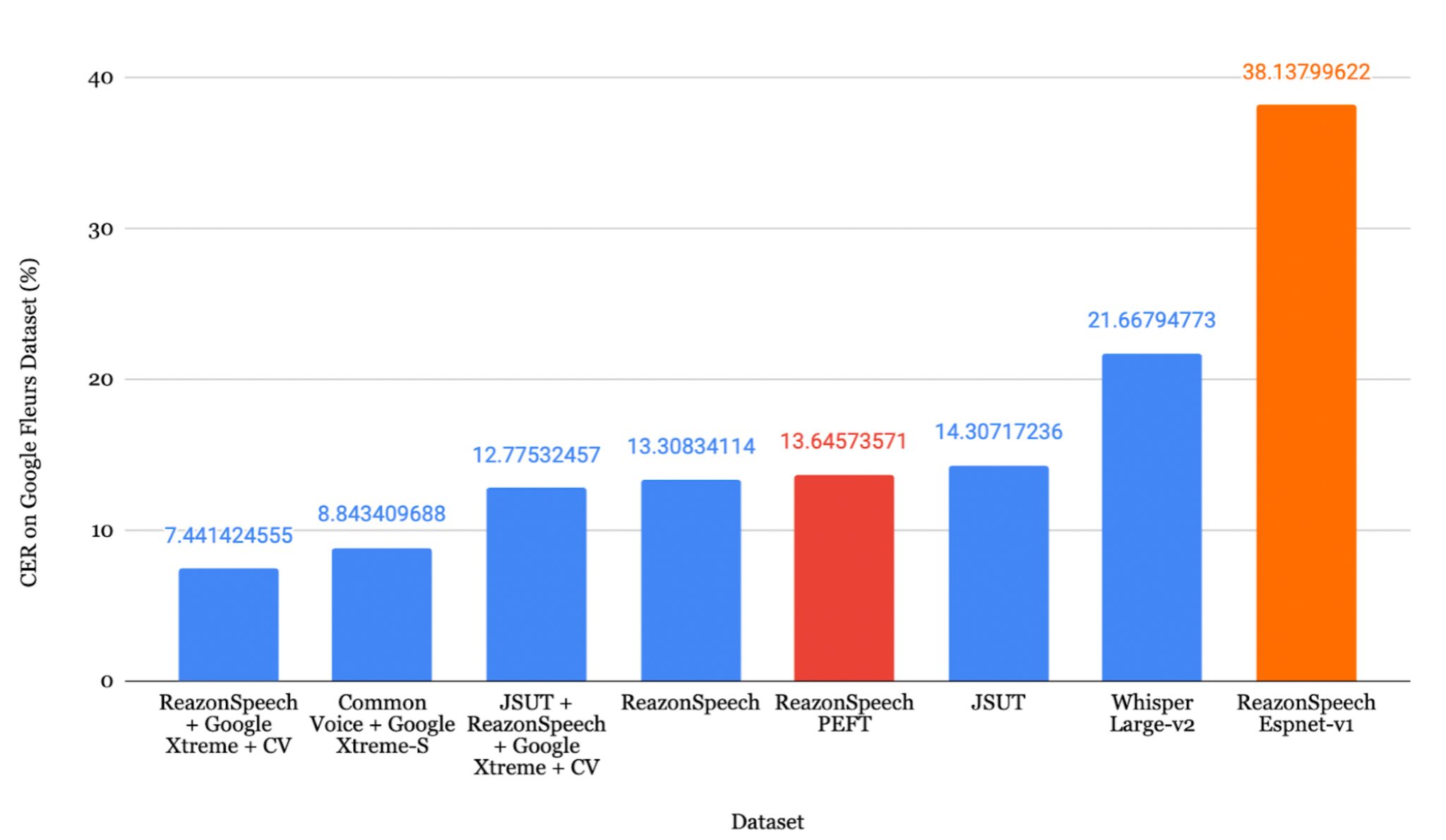
在 JSUT + ReazonSpeech + Google Xtreme + CV 数据集上微调的模型取得了最低 CER 8.15%。
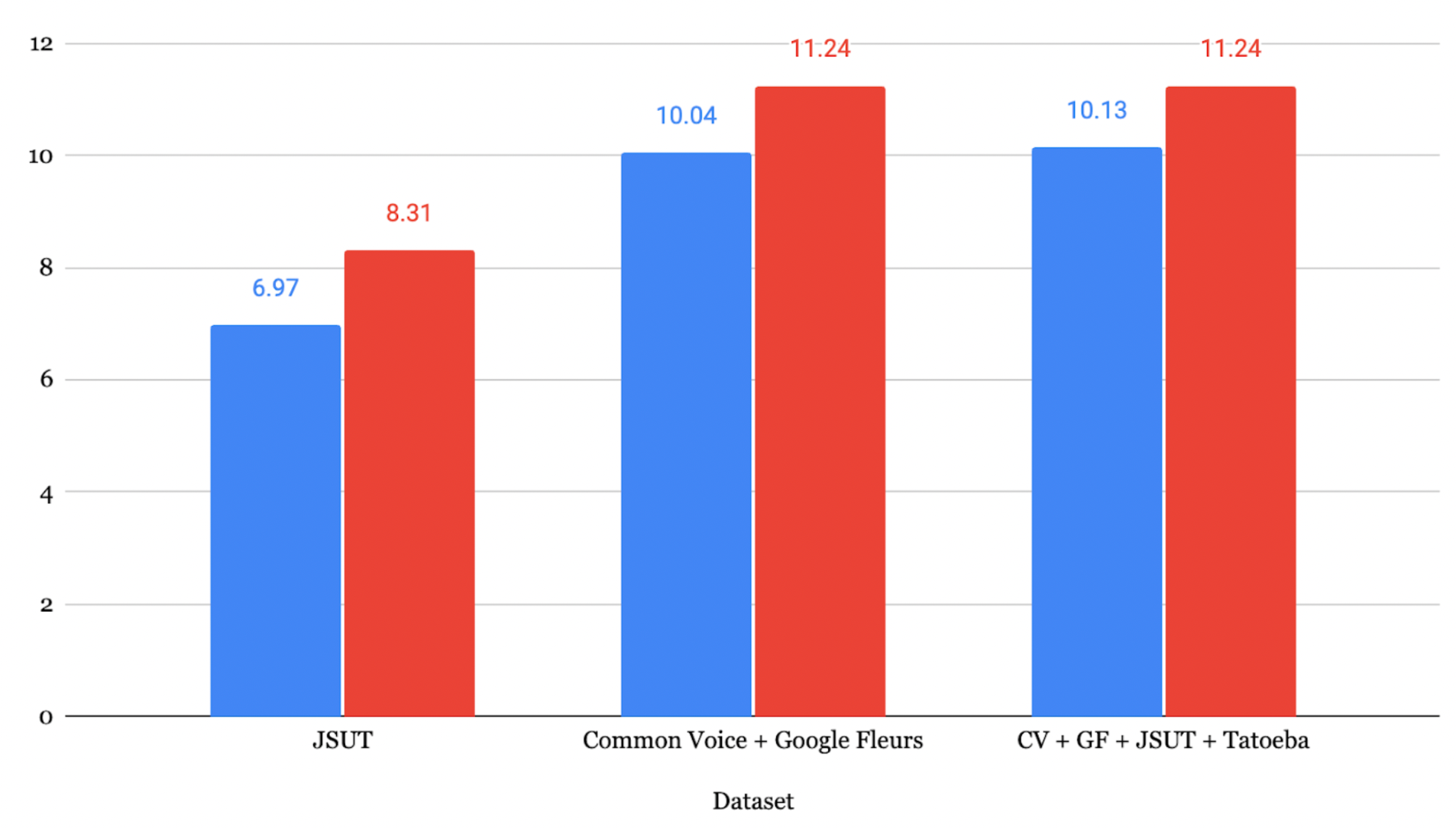
优化损失曲线
8. 评估
越南语评估
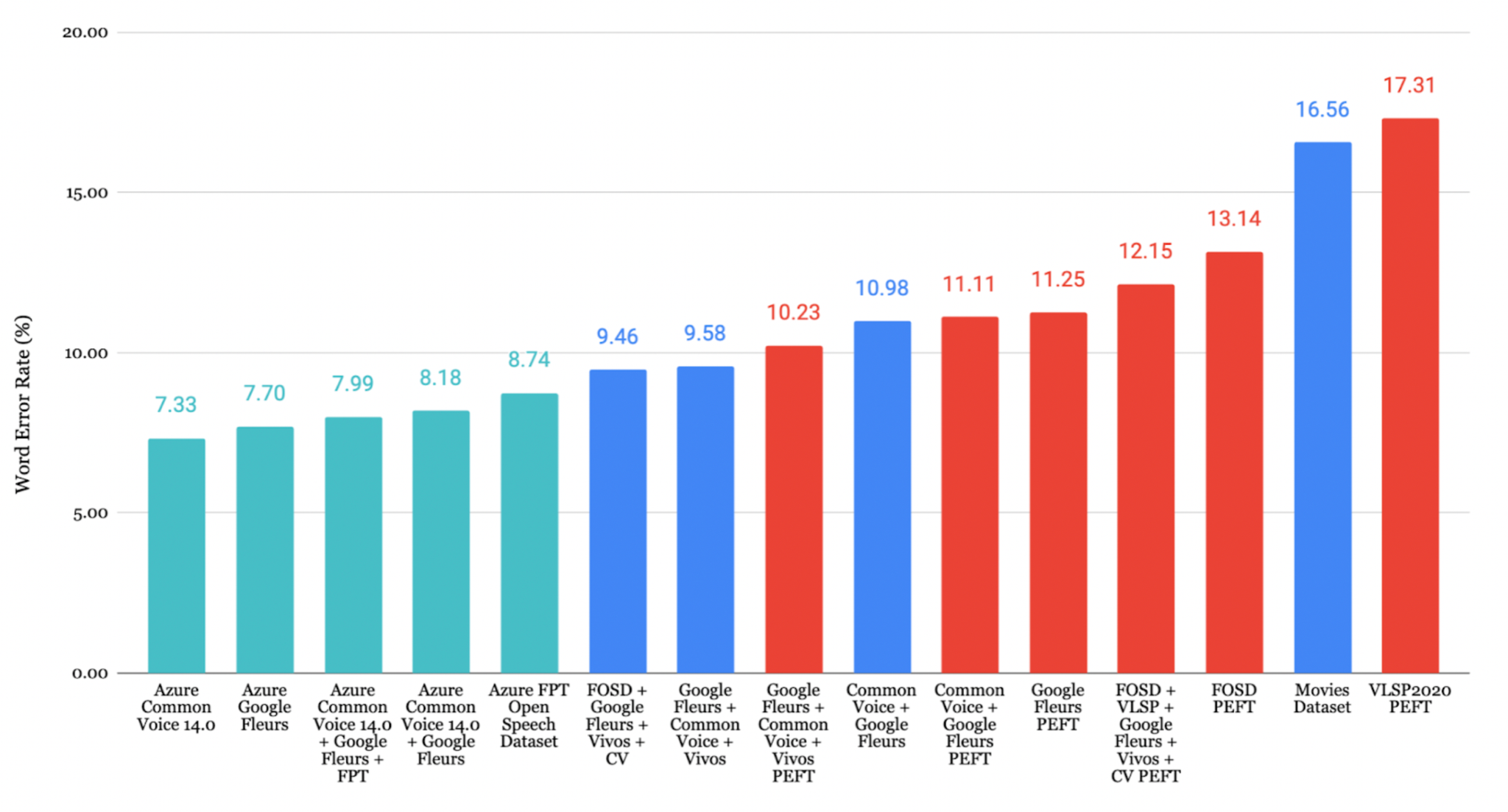
在所有评估数据集中,Google Fleurs + Common Voice + Vivos 组合取得了最低 CER 7.84%,表现出极高的转录准确度。
日语评估
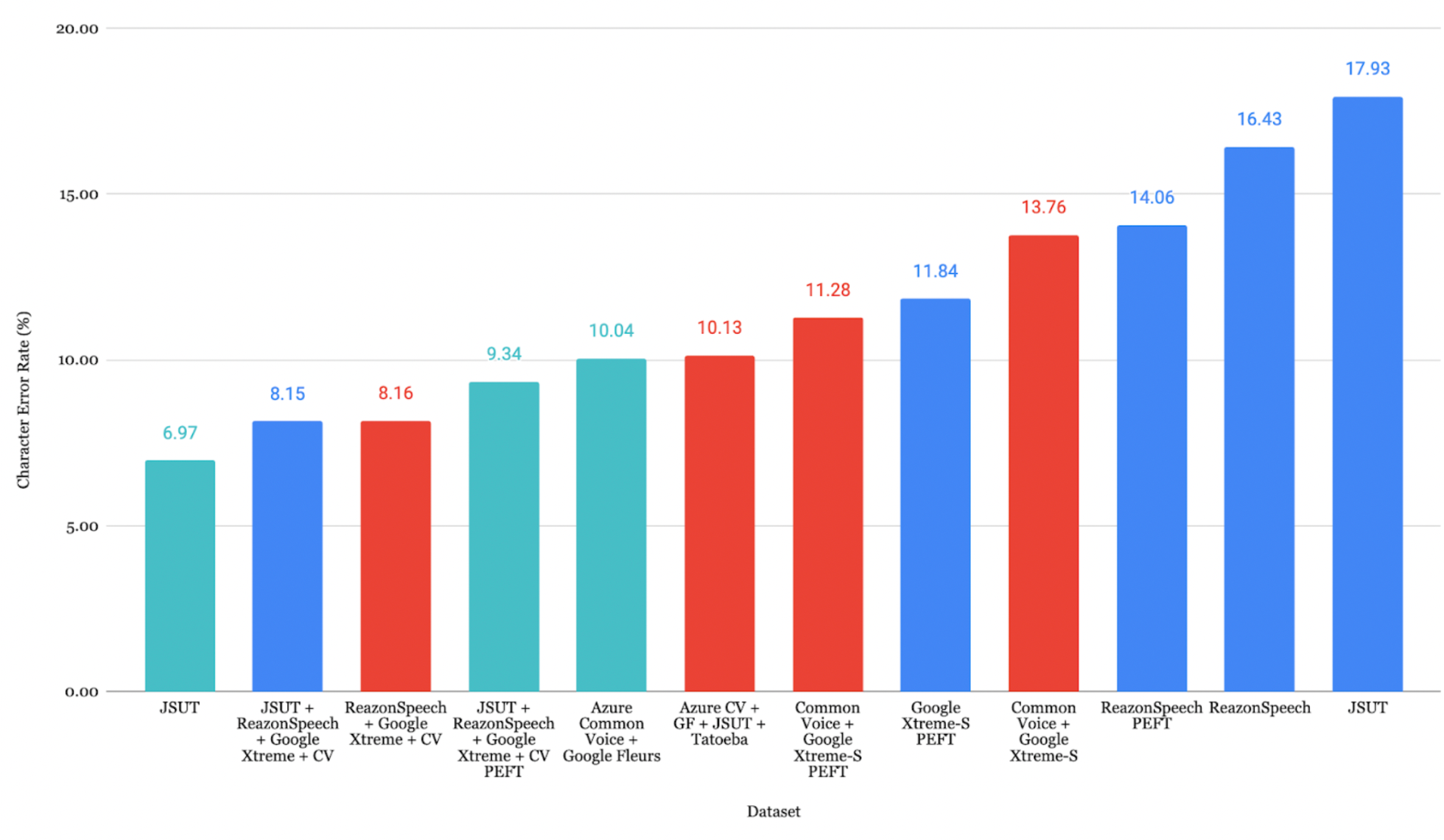
ReazonSpeech + Google Xtreme + CV 组合取得了最低 CER 7.44%。
Faster-Whisper 转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from ctranslate2.converters import TransformersConverter
model_id = "./whisper-fine-tuned/checkpoint-5000"
output_dir = "whisper-ct2"
converter = TransformersConverter(model_id, load_as_float16=True)
converter.convert(output_dir, quantization="float16")
model = WhisperModel(output_dir, device="cuda", compute_type="float16")
|
注意: Faster Whisper 在保持同等精度的前提下,推理速度比标准微调 Whisper 提升约 40%。
9. Azure Speech Studio
Azure Speech Studio 为 ASR 模型微调提供了另一种方案。
使用 Azure 进行转录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import os, evaluate
from azure.cognitiveservices.speech import SpeechConfig, SpeechRecognizer, AudioConfig
subscription_key = "your_subscription_key"
location = "japaneast"
endpoint = "your_endpoint"
config = SpeechConfig(subscription=subscription_key, region=location)
config.endpoint_id = endpoint
speech_config = SpeechConfig(
subscription=subscription_key,
region=location,
speech_recognition_language="ja-JP"
)
predictions = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(wav_base_path):
for file_name in files:
if file_name.endswith(".wav"):
audio_file_path = os.path.join(root, file_name)
audio_config = AudioConfig(filename=audio_file_path)
speech_recognizer = SpeechRecognizer(
speech_config=speech_config,
audio_config=audio_config
)
result = speech_recognizer.recognize_once()
if result.text:
predictions.append(result.text)
|
Azure 结果
越南语: 基于 Common Voice 14.0 训练的模型,WER 为 7.33%
日语: 基于 JSUT 训练的模型,CER 为 6.97%
注意: 虽然 Azure Speech Studio 在训练阶段的 WER 可能更低,但在面对多样化和复杂的未知音频数据时,Whisper 往往表现出更好的泛化能力。
10. 总结
Whisper ASR 模型的微调被证明是提升性能的有效技术手段。主要发现如下:
- DeepL 在中文到英文翻译中表现最为出色
- 微调能够带来一致的性能提升(越南语 WER 7.33-12.15%,日语 CER 8.15-17.93%)
- 数据增强通过 audiomentations 库引入了有价值的数据多样性
- 数据集质量至关重要:数据量、音频清晰度和主题多样性均会影响最终性能
- Whisper 在实际应用场景中表现更优,面对未知数据时优于 Azure
参考文献
- Radford, A., et al. (2022). Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision. arXiv:2212.04356
- Ardila, R., et al. (2020). Common Voice: A Massively-Multilingual Speech Corpus. arXiv:1912.06670
- Conneau, A., et al. (2022). FLEURS: Few-Shot Learning Evaluation of Universal Representations of Speech. arXiv:2205.12446
- Gandhi, S. (2022). Fine-Tune Whisper for Multilingual ASR with Transformers. Hugging Face Blog
- Mangrulkar, S. & Paul, S. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Using PEFT. Hugging Face Blog