概要
本研究では、機械翻訳の品質を正確に評価するとともに、人間による翻訳と同等の精度を目指して改善に取り組んでいます。5つの異なるベンチマーク翻訳モデルを採用し、3つの異なる評価指標でそれらの性能を測定しました。また、先行研究から得られた知見をもとに、モデルの精度向上にも取り組んでいます。
目次
- はじめに
- データセット
- 機械翻訳精度の評価方法
- 3.1. BLEU スコア
- 3.2. BLEURT スコア
- 3.3. COMET スコア
- 5つの基本的な機械翻訳モデルとその精度
- 4.1. Azure ベースラインモデル
- 4.2. Azure カスタムモデル
- 4.3. DeepL モデル
- 4.4. Google 翻訳
- 4.5. GPT-4 モデル
- 4.6. 比較と考察
- 機械翻訳精度の改善
- 5.1. GPT-4 のインコンテキスト学習
- 5.2. ハイブリッドモデル
- 5.3. データクリーニングツールとしてのGPT-4
- 結論
- 参考文献
1. はじめに
AI技術の進歩、特にOpenAIによるChatGPTの登場以降、AI業界への信頼は急速に高まっています。自然言語処理の中核的な技術である機械翻訳は、ますます重要性を増しています。
本論文では、多角的な評価指標を用いて5つの基本的な翻訳モデルを評価し、それらのモデルの精度を最大限に高めるための手法についても検討します。
2. データセット
本研究では、Hugging Faceで公開されているOpus100(ZH-EN)データセットを使用しています。このデータセットは、さまざまな分野にわたる100万件の中国語から英語への翻訳インスタンスで構成されており、翻訳モデルの学習に適した選択肢です。

注意: データセット内には翻訳の不正確な箇所が含まれていることに留意する必要があります。これらの不正確さは一見すると学習精度を低下させるように思えますが、同時にオーバーフィッティングの抑制にも寄与しています。
また、Azure AIプラットフォームへ統合する前に、各文に含まれる異常な記号を除去する前処理が必要です。
3. 機械翻訳精度の評価方法
多数の翻訳モデルの中から特定の目的に最適なものを選択するのは容易ではありません。翻訳モデルの評価には、主に2つのアプローチがあります。
- 従来の手法:BLEU スコア
- ニューラル指標:BLEURT スコアおよびCOMET スコア
3.1 BLEU スコア
BLEU(Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)は、ある自然言語から別の自然言語に機械翻訳されたテキストの品質を評価するアルゴリズムです(Papineni et al., 2002)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import nltk
bleu_scores = []
for reference, pre in zip(reference_translations, prediction):
reference_tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(reference.lower())
pre_tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(pre.lower())
if not reference_tokens or not pre_tokens:
continue
bleu_score = nltk.translate.bleu_score.sentence_bleu(
[reference_tokens], pre_tokens,
smoothing_function=nltk.translate.bleu_score.SmoothingFunction().method2)
bleu_scores.append(bleu_score)
average_bleu_score = sum(bleu_scores) / len(bleu_scores)
print("Average BLEU score:", average_bleu_score)
|
7つの平滑化関数
| 関数 | 説明 |
|---|
| Smoothing Function 1 | 加法(ラプラス)平滑化 - ゼロ確率を防ぐために定数値を加算 |
| Smoothing Function 2 | NIST平滑化 - 参照文長によるペナルティを導入 |
| Smoothing Function 3 | Chen and Cherry - 候補翻訳の長さに応じて適応 |
| Smoothing Function 4 | JenLin - 加法的手法と調整手法のバランスを取る |
| Smoothing Function 5 | Gao and He - 短い翻訳へのバイアスに対処 |
| Smoothing Function 6 | ベイズ的手法 - 長い文に対して頑健な推定を提供 |
| Smoothing Function 7 | 幾何平均 - n-gram精度の幾何平均を算出 |
注意: BLEUには限界があります。語順や構文を考慮せず、主にn-gramの一致に依存するため、流暢さ、慣用表現、文法、全体的な一貫性を捉えることができません。
3.2 BLEURT スコア
BLEURTは、自然言語生成のための評価指標です。参照文と候補文のペアを入力として受け取り、流暢さと意味の保持度を示すスコアを返します(Sellam, 2021)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from bleurt import score
checkpoint = "/path/to/BLEURT-20"
scorer = score.BleurtScorer(checkpoint)
scores = scorer.score(references=reference_translations, candidates=prediction)
total_score = sum(scores) / len(scores)
print("Total Score:", total_score)
|
ヒント: BLEURTを使用するには、事前にTensorFlowのインストールが必要です。
3.3 COMET スコア
COMETは、多言語機械翻訳評価モデルを学習するためのニューラルフレームワークであり、翻訳品質に対する人間の判定を予測するよう設計されています。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from comet import download_model, load_from_checkpoint
model_path = download_model("Unbabel/wmt22-comet-da")
model = load_from_checkpoint(model_path)
data = []
for src, pre, reference in zip(source_sentences, preds, reference_translations):
data.append({
"src": src,
"mt": pre,
"ref": reference
})
model_output = model.predict(data, batch_size=8, gpus=0)
print(model_output)
|
4. 5つの基本的な機械翻訳モデルとその精度
4.1 Azure ベースラインモデル
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import requests, uuid, json
endpoint = ""
subscription_key = ""
location = ""
path = '/translate'
constructed_url = endpoint + path
params = {
'api-version': '3.0',
'from': 'zh',
'to': 'en'
}
headers = {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': subscription_key,
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region': location,
'Content-type': 'application/json',
'X-ClientTraceId': str(uuid.uuid4())
}
body = []
for i in source_sentences:
body.append({'text': i})
request = requests.post(constructed_url, params=params, headers=headers, json=body)
response = request.json()
|
4.2 Azure カスタムモデル
Azure カスタムモデルは、追加データセットを使用してAzure ベースラインモデルをさらに学習させた改良版です。Azure プラットフォーム上でのカスタムモデルのBLEUスコアは 39.45 です。
注意: カスタムモデルを使用する場合、APIから呼び出すためにはAzure プラットフォーム上で公開する必要があります。
4.3 DeepL モデル
DeepL 翻訳は、畳み込みニューラルネットワークと英語ピボットを使用するニューラル機械翻訳サービスです。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import deepl
API_KEY = 'your-api-key'
source_lang = 'ZH'
target_lang = 'EN-US'
translator = deepl.Translator(API_KEY)
results = translator.translate_text(source_sentences, source_lang=source_lang, target_lang=target_lang)
|
4.4 Google 翻訳
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import requests
def translate_texts(texts, target_language):
api_key = 'your-api-key'
url = 'https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2'
translations = []
for text in texts:
params = {
'key': api_key,
'q': text,
'target': target_language
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
translated_text = data['data']['translations'][0]['translatedText']
translations.append(translated_text)
return translations
|
4.5 GPT-4 モデル
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import openai
def translate_text(text_list):
openai.api_key = 'your-api-key'
translations = []
for text in text_list:
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a translation assistant from Chinese to English. Some rules to remember:\n\n- Do not add extra blank lines.\n- It is important to maintain the accuracy of the contents, but we don't want the output to read like it's been translated. So instead of translating word by word, prioritize naturalness and ease of communication."},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=messages,
max_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
timeout=30
)
choices = response['choices']
if len(choices) > 0:
translation = choices[0]['message']['content']
translations.append(translation)
return translations
|
注意: GPT-4は他の4つのモデルと比較して応答速度が遅い傾向があります。また、トークン数が過剰になるとオーバーロードが発生する可能性があります。
4.6 比較と考察
評価結果に基づくと:
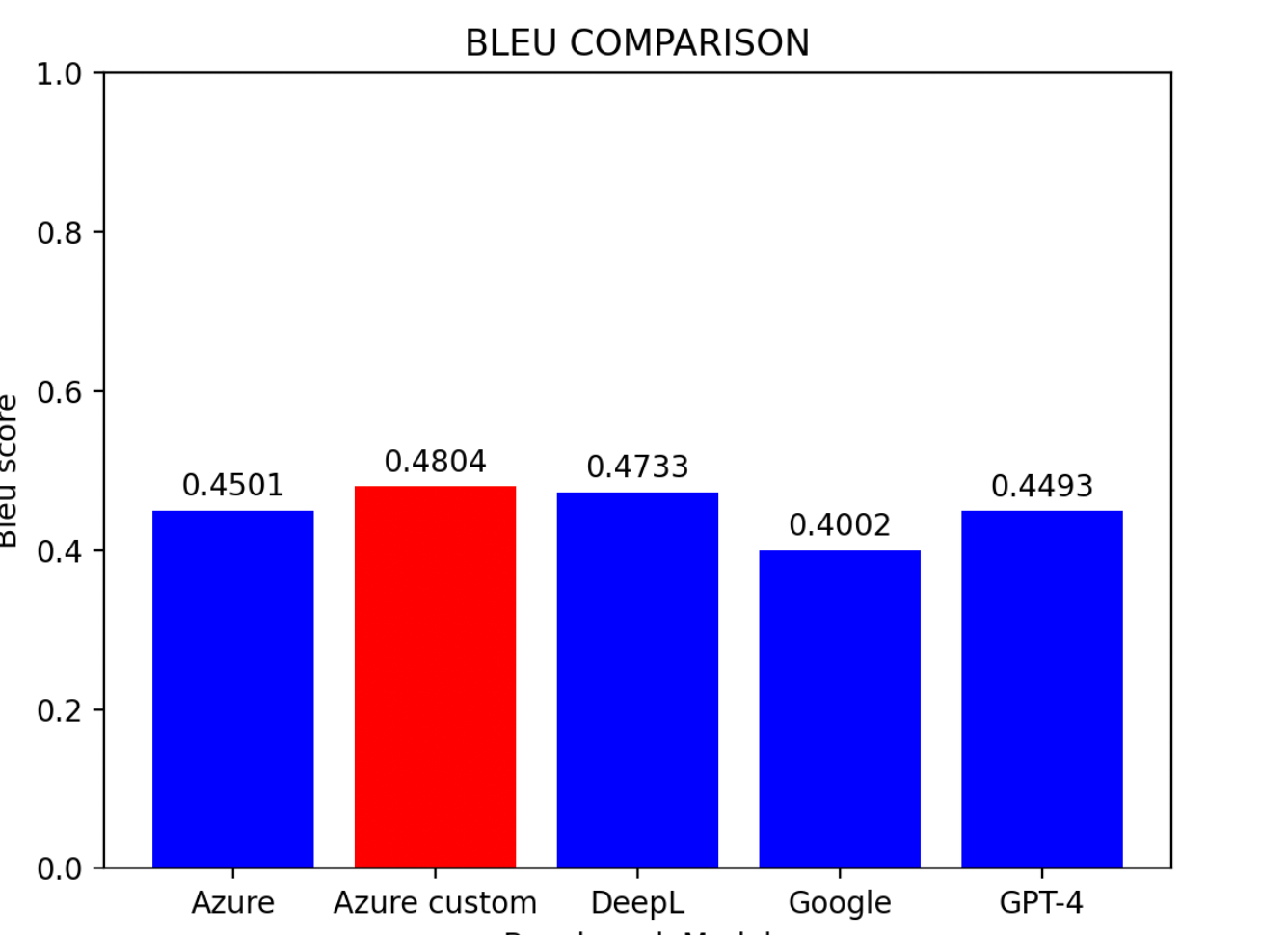
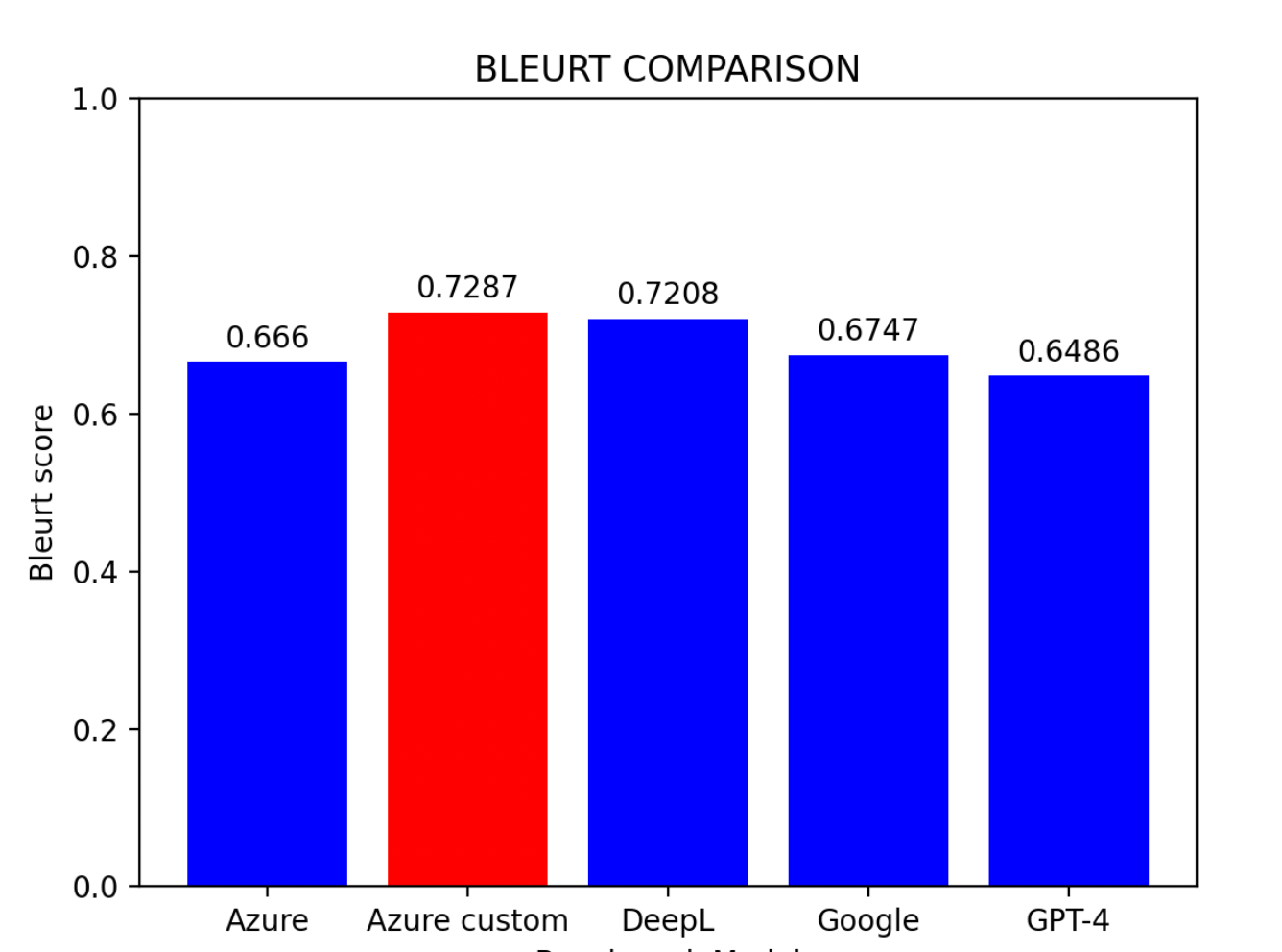
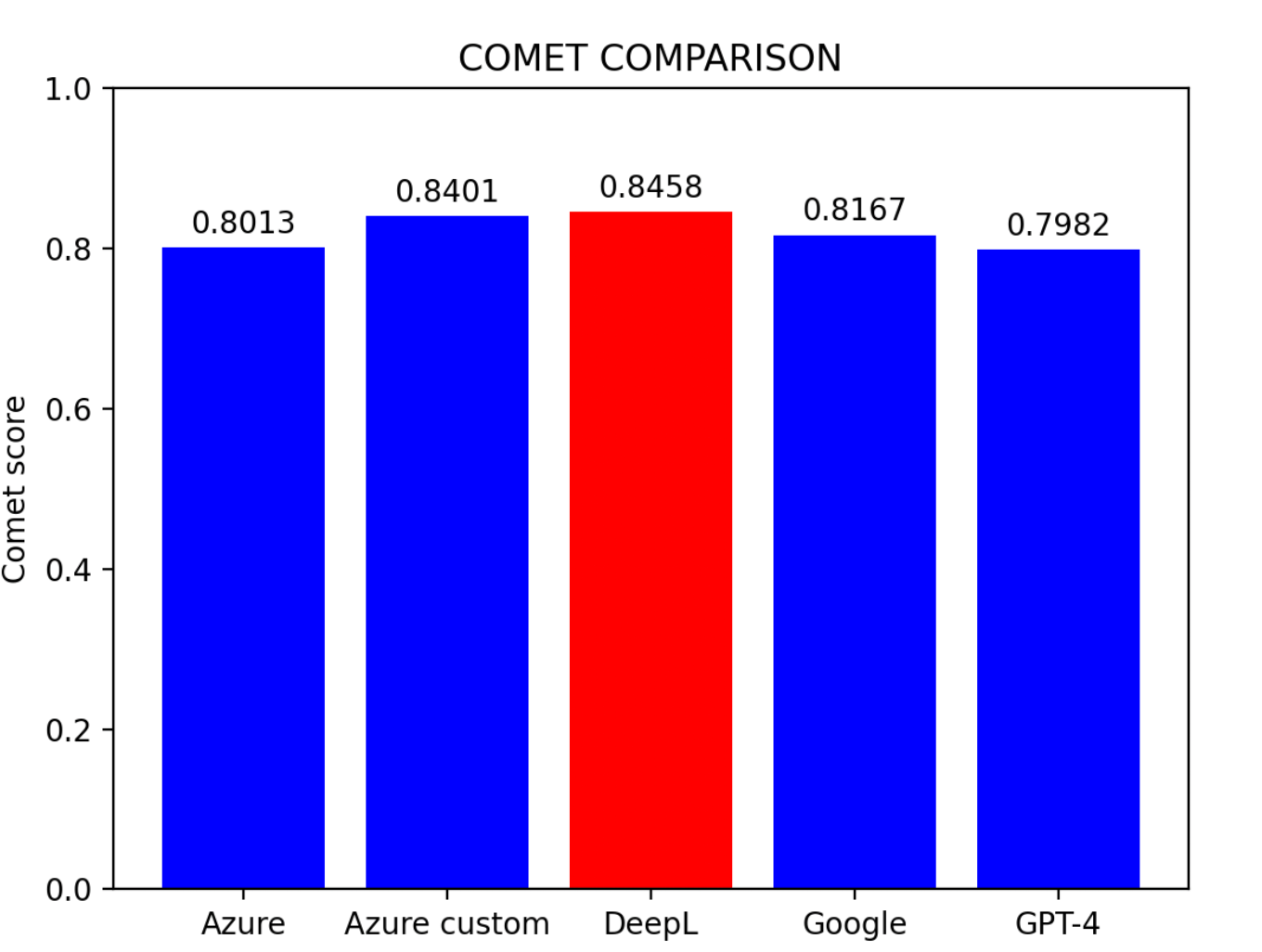
主な発見:
- Azure カスタムモデルが最も高い性能を示した
- DeepLが僅差で2位
- Azure ベースラインモデルが3位
- Google 翻訳とGPT-4は同程度の成績
ヒント: 事前学習の環境がないユーザーにとって、DeepLは現時点で中国語から英語への翻訳に最も効果的なモデルです。
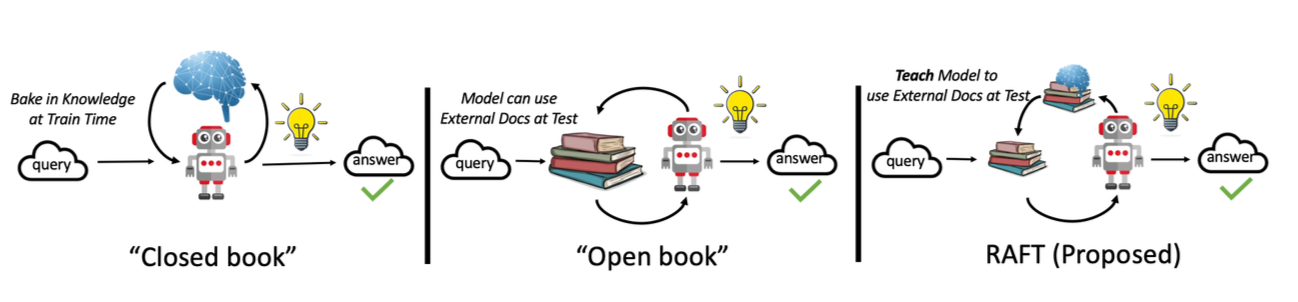
5. 機械翻訳精度の改善
翻訳精度を向上させるための3つのアプローチを検討しました。
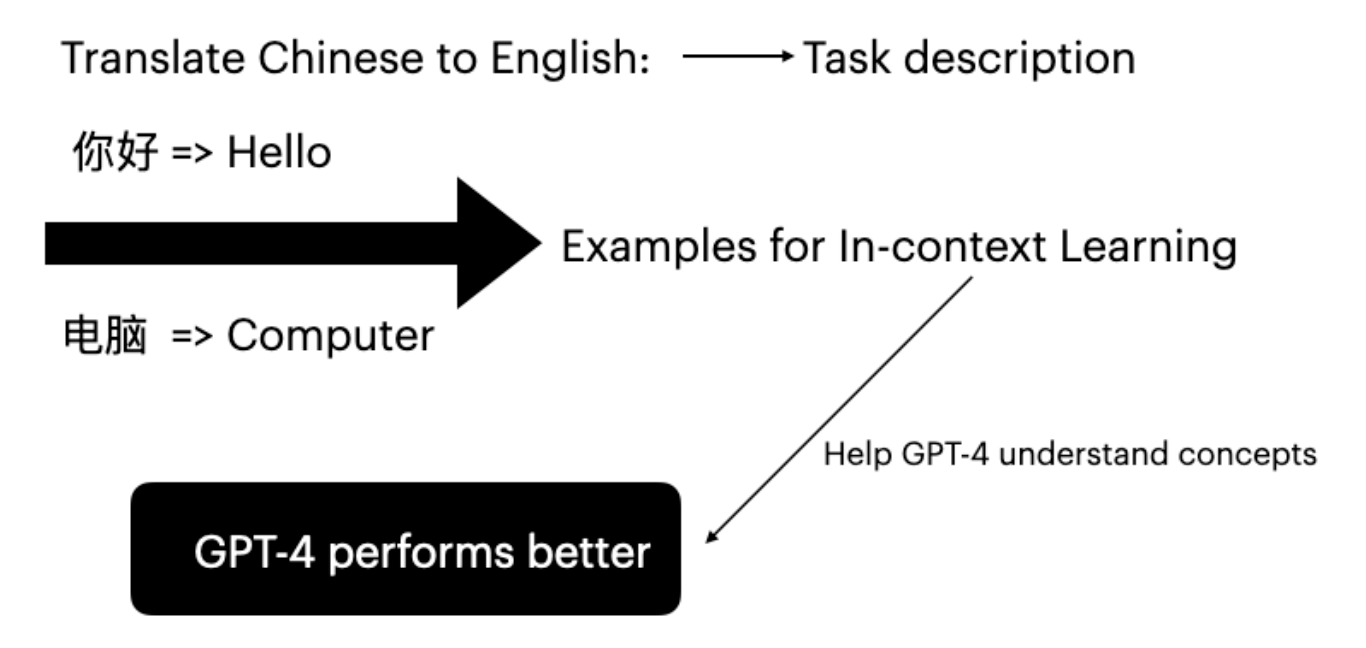
5.1 GPT-4 のインコンテキスト学習
大規模言語モデルは、プロンプト内に特定のタスク例を提示するインコンテキスト学習により性能を向上させることができます(Brown et al., 2020)。
結果: BLEURTスコアが0.6486から0.6755に向上し、インコンテキスト学習の有効性が確認されました。
5.2 ハイブリッドモデル
ハイブリッド閾値モデルでは、特定の閾値を設定し、ある文がその閾値を下回った場合に別のモデルで再翻訳を行います。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import requests, uuid, json
import openai
from comet import download_model, load_from_checkpoint
def translate_with_fallback(text):
translation_from_Azure = Azure_translation(text)
model_path = download_model("Unbabel/wmt22-comet-da")
model = load_from_checkpoint(model_path)
refined_translation = []
indices_to_correct = []
for i in range(len(translation_from_Azure)):
data = [{
"src": source_sentences[i],
"mt": translation_from_Azure[i],
"ref": reference_translations[i]
}]
res = model.predict(data, batch_size=1, gpus=0)
if res.scores[0] < 0.81:
indices_to_correct.append(i)
sentences_to_correct = [source_sentences[i] for i in indices_to_correct]
corrected_sentences = gpt_translation(sentences_to_correct)
corrected_index = 0
for i in range(len(translation_from_Azure)):
if i in indices_to_correct:
refined_translation.append(corrected_sentences[corrected_index])
corrected_index += 1
else:
refined_translation.append(translation_from_Azure[i])
return refined_translation
|
ハイブリッドモデルの考察
- 最適な閾値はCOMETスコアと一致する
- Azure カスタム + DeepLまたはDeepL + GPT-4の組み合わせが最良の結果を示した
- ほぼすべてのハイブリッドモデルが単一モデルを上回った
- 閾値を高くしてもスコアが必ずしも改善されるわけではない
5.3 データクリーニングツールとしてのGPT-4
GPT-4を使用してデータセットの前処理を行い、不正確な翻訳を修正することができます。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import openai
import json
pair = {}
for zh, en in zip(source_sentences, reference_translations):
pair[zh] = en
def translate_text(pair):
openai.api_key = 'your-api-key'
translations = []
for zh, en in pair.items():
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Chinese to English translation corrector. You need to modify the incorrect English translations below and correct it by given Chinese sentences, please remember not to use English abbreviations and not add extra blank lines. Fix weird punctuation. And the result should be English sentences only"},
{"role": "user", "content": json.dumps({"zh": zh, "en": en})}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=messages,
max_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
timeout=30
)
choices = response['choices']
if len(choices) > 0:
model_response = choices[0]['message']['content']
translations.append(model_response)
return translations
|
ヒント: GPT-4を活用した原文と訳文両方のデータクリーニングは効果的です。精製されたデータセットを使用すると、Azure ベースラインのスコアがDeepLの未精製データセットでのスコアに匹敵するレベルに達します。
6. 結論
本論文では、3つの評価指標と5つのベンチマークモデルを用いて、機械翻訳精度と改善手法を検証しました。
主な結論:
- DeepLが中国語から英語への翻訳で最も優れた性能を示した
- Azure ベースラインモデルは十分なデータと適切な学習によって高い性能を達成できる
- 異なる翻訳エンジンを組み合わせたハイブリッドモデルは精度を向上させる
- GPT-4によるデータクリーニングはデータセットの品質を改善し、モデル性能の向上につながる
注意: 本研究には限界があります。目視検査の結果、高いスコアを得ていても翻訳品質が伴っていないケースが確認されました。また、一部の精度改善手法ではスコアが低下する場合もありました。
7. 参考文献
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W. J. (2002). BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL).
Thibault Sellam (2021). BLEURT
Tom Brown et al. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners.
Daniel Bashir (2023). In-Context Learning, in Context. The Gradient.
Amr Hendy et al. (2023). How Good Are GPT Models at Machine Translation? A Comprehensive Evaluation. Microsoft.
Ricardo Rei (2022). COMET