概要
コミュニケーション技術が急速に進化する中、OpenAI Whisperモデルをはじめとする最新技術により、多言語音声テキスト変換の精度とアクセシビリティは大幅に向上しました。しかし、特に認識精度の面ではまだ改善の余地があります。本研究では、ベトナム語と日本語に焦点を当て、自動音声認識(ASR)モデルの性能向上に取り組みました。
評価には標準的な指標を使用しています。ベトナム語にはWord Error Rate(WER)、日本語にはCharacter Error Rate(CER)を採用しました。
主要な結果:
- ベトナム語(FOSD + Common Voice + Google Fleurs + Vivos): WER 9.46%
- 日本語(ReazonSpeech + Common Voice + Google Fleurs): CER 8.15%
目次
- 背景
- 環境構築
- データセットの読み込み
- データ前処理
- 学習
- パラメータ効率的ファインチューニング
- 結果
- 評価
- Azure Speech Studio
- まとめ
1. 背景
現代社会においてコミュニケーションとテクノロジーは不可欠ですが、アクセシビリティ、包括性、効率的な知識共有においてはまだ多くの課題が残っています。自動音声認識(ASR)の進歩は、特にオンライン会議の場面で、人間とコンピュータのやり取りを効率化します。
ASRとは、音声信号を対応するテキストに変換する技術です。近年、大規模な音声データセットとその書き起こしデータの利用が容易になったことで、さまざまな企業がこの分野に注目しています。

OpenAI Whisperは、Transformerベースのエンコーダ・デコーダモデルであり、sequence-to-sequenceアーキテクチャとして設計されています。音声スペクトログラム特徴量を入力とし、テキストトークン列に変換します。この処理は以下のステップで構成されます。
- 特徴抽出器が生の音声データをlog-Melスペクトログラムに変換
- Transformerエンコーダがエンコーダ隠れ状態の系列を生成
- デコーダがcross-attentionメカニズムを用いてテキストトークンを予測
2. 環境構築
Whisperのファインチューニングには、Google Colabを利用する方法とローカルPCで実行する方法の2つのアプローチがあります。
必要なパッケージ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| python -m pip install -U pip
pip install evaluate pandas numpy huggingface_hub pydub tqdm spacy ginza audiomentations
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
pip install datasets>=2.6.1
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
pip install librosa
pip install evaluate>=0.30
pip install jiwer
pip install gradio
pip install -q bitsandbytes datasets accelerate loralib
pip install -q git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@main git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git@main
|
注: 本記事のファインチューニングには、Windows 11 Pro、AMD Ryzen 7 3700X 8コアプロセッサ、80GB RAM、GeForce RTX 3090搭載のPCを使用しました。
3. データセットの読み込み
方法1: Hugging Faceの利用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from datasets import load_dataset, DatasetDict
common_voice = DatasetDict()
common_voice["train"] = load_dataset(
"mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0", "ja",
split="train+validation", use_auth_token=True
)
common_voice["test"] = load_dataset(
"mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0", "ja",
split="test", use_auth_token=True
)
common_voice = common_voice.remove_columns([
"accent", "age", "client_id", "down_votes",
"gender", "locale", "path", "segment", "up_votes"
])
|
方法2: 手動でのデータセット準備
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import os, csv, codecs
def text_change_csv(input_path, output_path):
file_csv = os.path.splitext(output_path)[0] + ".csv"
output_dir = os.path.dirname(input_path)
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, file_csv)
encodings = ["utf-8", "latin-1"]
for encoding in encodings:
try:
with open(input_path, 'r', encoding=encoding) as rf:
with codecs.open(output_file, 'w', encoding=encoding, errors='replace') as wf:
readfile = rf.readlines()
for read_text in readfile:
read_text = read_text.split('|')
writer = csv.writer(wf, delimiter=',')
writer.writerow(read_text)
print(f"CSV has been created using encoding: {encoding}")
return True
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
|
使用データセット
| データセット | 言語 | 取得方法 | 音声時間 |
|---|
| Common Voice 13.0 | ベトナム語、日本語 | Hugging Face | 19時間(VN)、10時間(JP) |
| Google Fleurs | ベトナム語、日本語 | Hugging Face | 11時間(VN)、8時間(JP) |
| Vivos | ベトナム語 | Hugging Face | 15時間 |
| FPT Open Speech Dataset | ベトナム語 | ダウンロード&展開 | 30時間 |
| VLSP2020 | ベトナム語 | ダウンロード&展開 | 100時間 |
| ReazonSpeech | 日本語 | Hugging Face | 5時間 |
| JSUT | 日本語 | ダウンロード&展開 | 10時間 |
| JVS | 日本語 | ダウンロード&展開 | 30時間 |
4. データ前処理
データ拡張
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| from audiomentations import Compose, AddGaussianNoise, TimeStretch, PitchShift
common_voice = common_voice.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16000))
augment_waveform = Compose([
AddGaussianNoise(min_amplitude=0.005, max_amplitude=0.015, p=0.2),
TimeStretch(min_rate=0.8, max_rate=1.25, p=0.2, leave_length_unchanged=False),
PitchShift(min_semitones=-4, max_semitones=4, p=0.2)
])
def augment_dataset(batch):
audio = batch["audio"]["array"]
augmented_audio = augment_waveform(samples=audio, sample_rate=16000)
batch["audio"]["array"] = augmented_audio
return batch
common_voice['train'] = common_voice['train'].map(augment_dataset, keep_in_memory=True)
|
書き起こしの正規化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import string
def remove_punctuation(sentence):
translator = str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation)
modified_sentence = sentence.translate(translator)
return modified_sentence
def fix_sentence(sentence):
transcription = sentence
if transcription.startswith('"') and transcription.endswith('"'):
transcription = transcription[1:-1]
transcription = remove_punctuation(transcription)
transcription = transcription.lower()
return transcription
|
Whisper向けデータセット準備
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| def prepare_dataset(batch):
audio = batch["audio"]
batch["input_features"] = processor.feature_extractor(
audio["array"], sampling_rate=audio["sampling_rate"]
).input_features[0]
batch["input_length"] = len(audio["array"]) / audio["sampling_rate"]
transcription = fix_sentence(batch["transcription"])
batch["labels"] = processor.tokenizer(
transcription, max_length=225, truncation=True
).input_ids
return batch
common_voice = common_voice.map(
prepare_dataset,
remove_columns=common_voice.column_names['train'],
num_proc=1,
keep_in_memory=True
)
|
5. 学習
Data Collator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import torch
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Union
@dataclass
class DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding:
processor: Any
def __call__(self, features: List[Dict[str, Union[List[int], torch.Tensor]]]) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
input_features = [{"input_features": feature["input_features"]} for feature in features]
batch = self.processor.feature_extractor.pad(input_features, return_tensors="pt")
label_features = [{"input_ids": feature["labels"]} for feature in features]
labels_batch = self.processor.tokenizer.pad(label_features, return_tensors="pt")
labels = labels_batch["input_ids"].masked_fill(labels_batch.attention_mask.ne(1), -100)
if (labels[:, 0] == self.processor.tokenizer.bos_token_id).all().cpu().item():
labels = labels[:, 1:]
batch["labels"] = labels
return batch
data_collator = DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding(processor=processor)
|
評価指標(ベトナム語 - WER)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import evaluate
metric = evaluate.load("wer")
def compute_metrics(pred):
pred_ids = pred.predictions
label_ids = pred.label_ids
label_ids[label_ids == -100] = tokenizer.pad_token_id
pred_str = tokenizer.batch_decode(pred_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
label_str = tokenizer.batch_decode(label_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=pred_str, references=label_str)
return {"wer": wer}
|
評価指標(日本語 - CER)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import spacy, ginza
nlp = spacy.load("ja_ginza")
ginza.set_split_mode(nlp, "C")
def compute_metrics(pred):
pred_ids = pred.predictions
label_ids = pred.label_ids
label_ids[label_ids == -100] = processor.tokenizer.pad_token_id
pred_str = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(pred_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
label_str = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(label_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# 日本語テキストを適切にトークン化して評価
pred_str = [" ".join([str(i) for i in nlp(j)]) for j in pred_str]
label_str = [" ".join([str(i) for i in nlp(j)]) for j in label_str]
wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=pred_str, references=label_str)
return {"wer": wer}
|
学習パラメータ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| from transformers import Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
model.config.dropout = 0.05
training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
output_dir="./whisper-fine-tuned",
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
gradient_accumulation_steps=1,
learning_rate=1e-6,
lr_scheduler_type='linear',
optim="adamw_bnb_8bit",
warmup_steps=200,
num_train_epochs=5,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
fp16=True,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
predict_with_generate=True,
generation_max_length=255,
eval_steps=500,
logging_steps=500,
report_to=["tensorboard"],
load_best_model_at_end=True,
metric_for_best_model="wer",
greater_is_better=False,
push_to_hub=False,
save_total_limit=1
)
|
ヒント: 主要な学習パラメータについて:
- learning_rate: 1e-5または1e-6が最適
- warmup_steps: 全ステップ数の10%程度に設定
- per_device_train_batch_size: GPUの容量に応じて設定(RTX 3090では16)
- dropout: 過学習防止に0.05または0.10を使用
6. パラメータ効率的ファインチューニング(PEFT)
PEFTは**全パラメータのわずか1%**のみを学習対象としながら、同等の性能を達成します。
| 通常のファインチューニング | パラメータ効率的ファインチューニング |
|---|
| 学習時間が短い | 学習時間が長い |
| 大きな計算リソースが必要 | 少ない計算リソースで実行可能 |
| モデル全体を再学習 | パラメータの一部のみを更新 |
| 過学習しやすい | 過学習しにくい |
LoRAの設定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| from transformers import WhisperForConditionalGeneration, prepare_model_for_int8_training
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path, load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto"
)
model = prepare_model_for_int8_training(model)
def make_inputs_require_grad(module, input, output):
output.requires_grad_(True)
model.model.encoder.conv1.register_forward_hook(make_inputs_require_grad)
config = LoraConfig(
r=32,
lora_alpha=64,
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none"
)
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# Output: trainable params: 15728640 || all params: 1559033600 || trainable%: 1.01%
|
7. 結果
ベトナム語の結果
FOSD + Google Fleurs + Vivos + CVデータセットでファインチューニングしたモデルが、最も低いWER 9.46% を達成しました。
日本語の結果
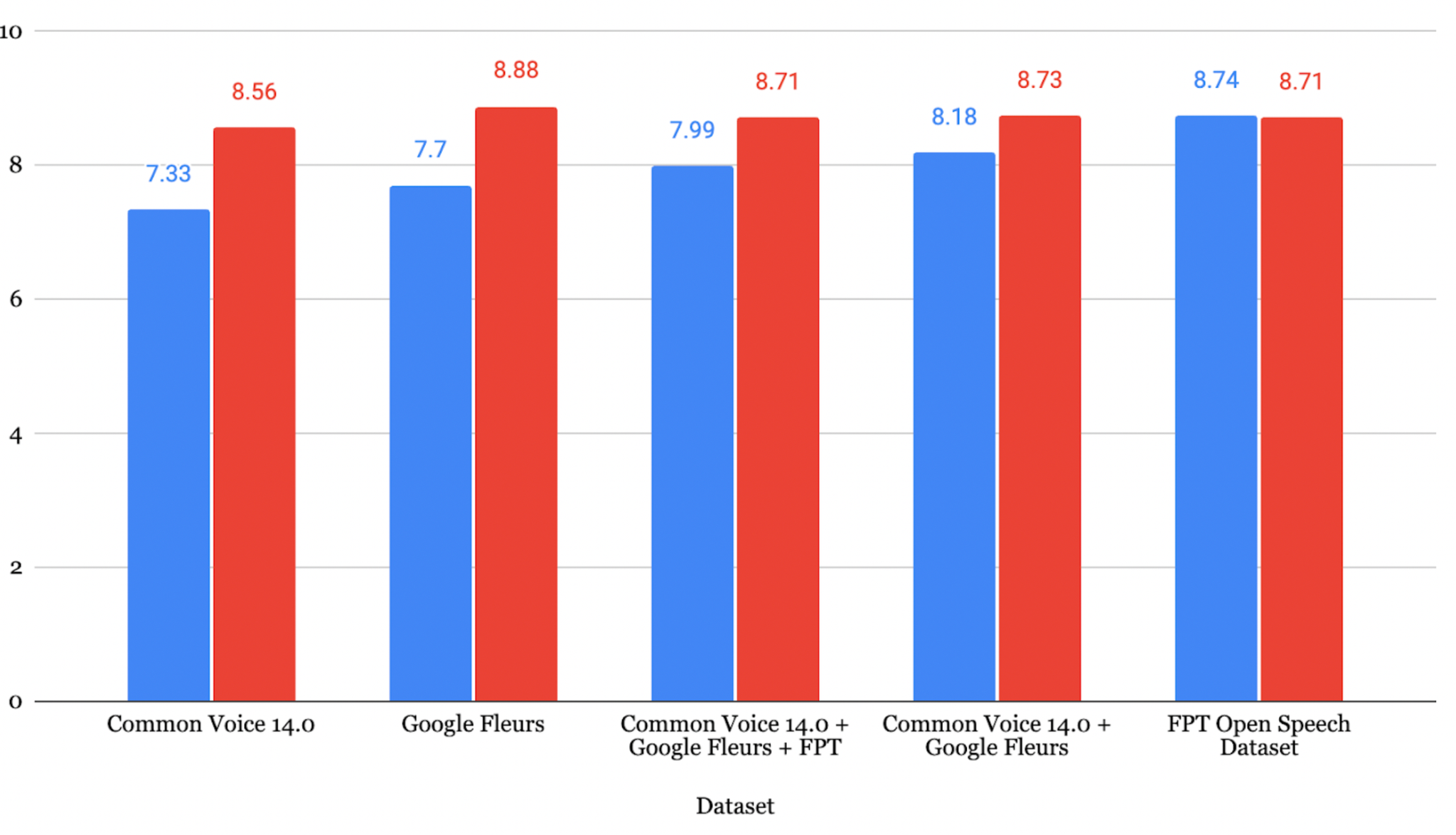
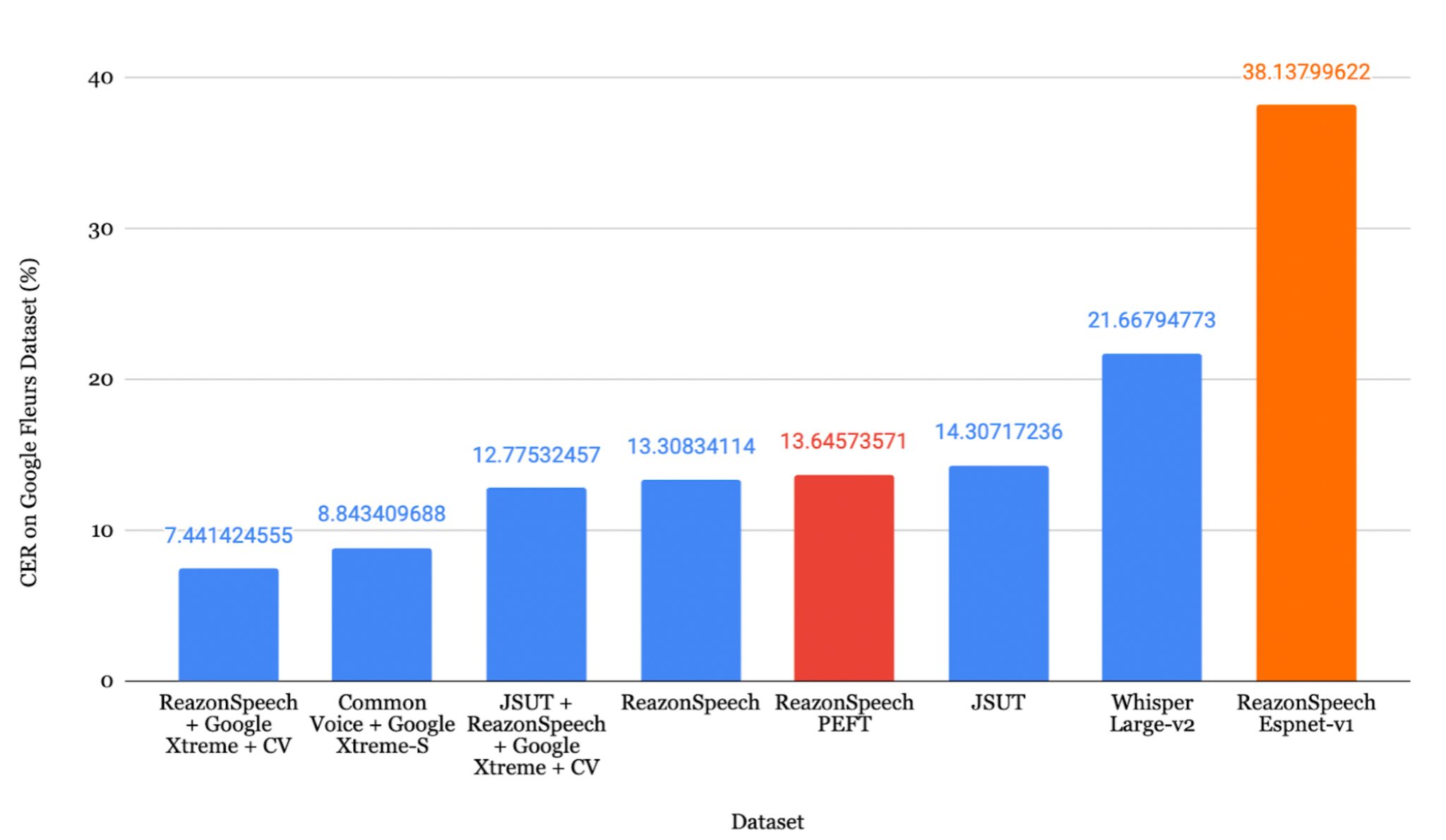
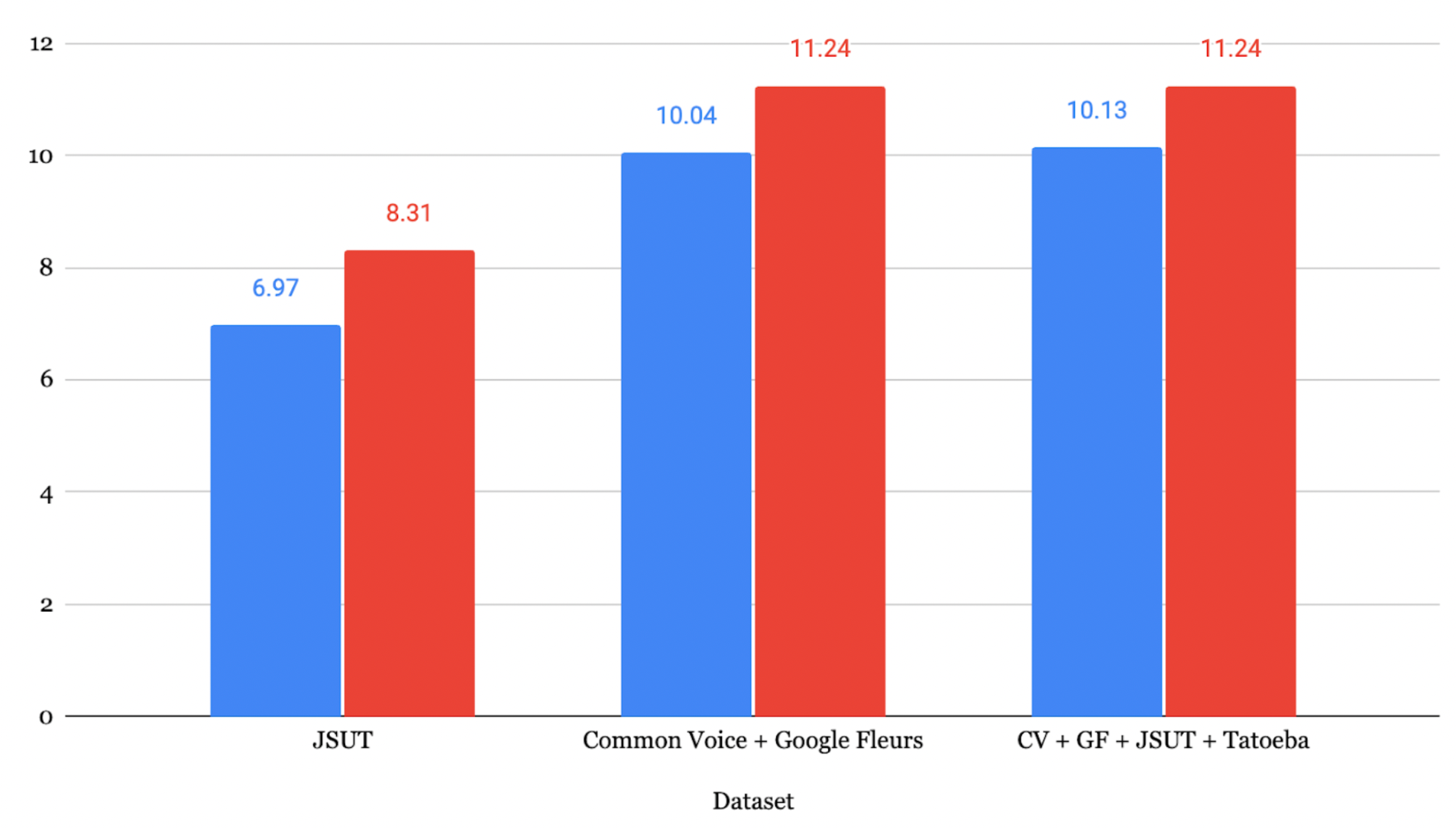
JSUT + ReazonSpeech + Google Xtreme + CVデータセットでファインチューニングしたモデルが、最も低いCER 8.15% を達成しました。
最適化ロス曲線
8. 評価
ベトナム語の評価
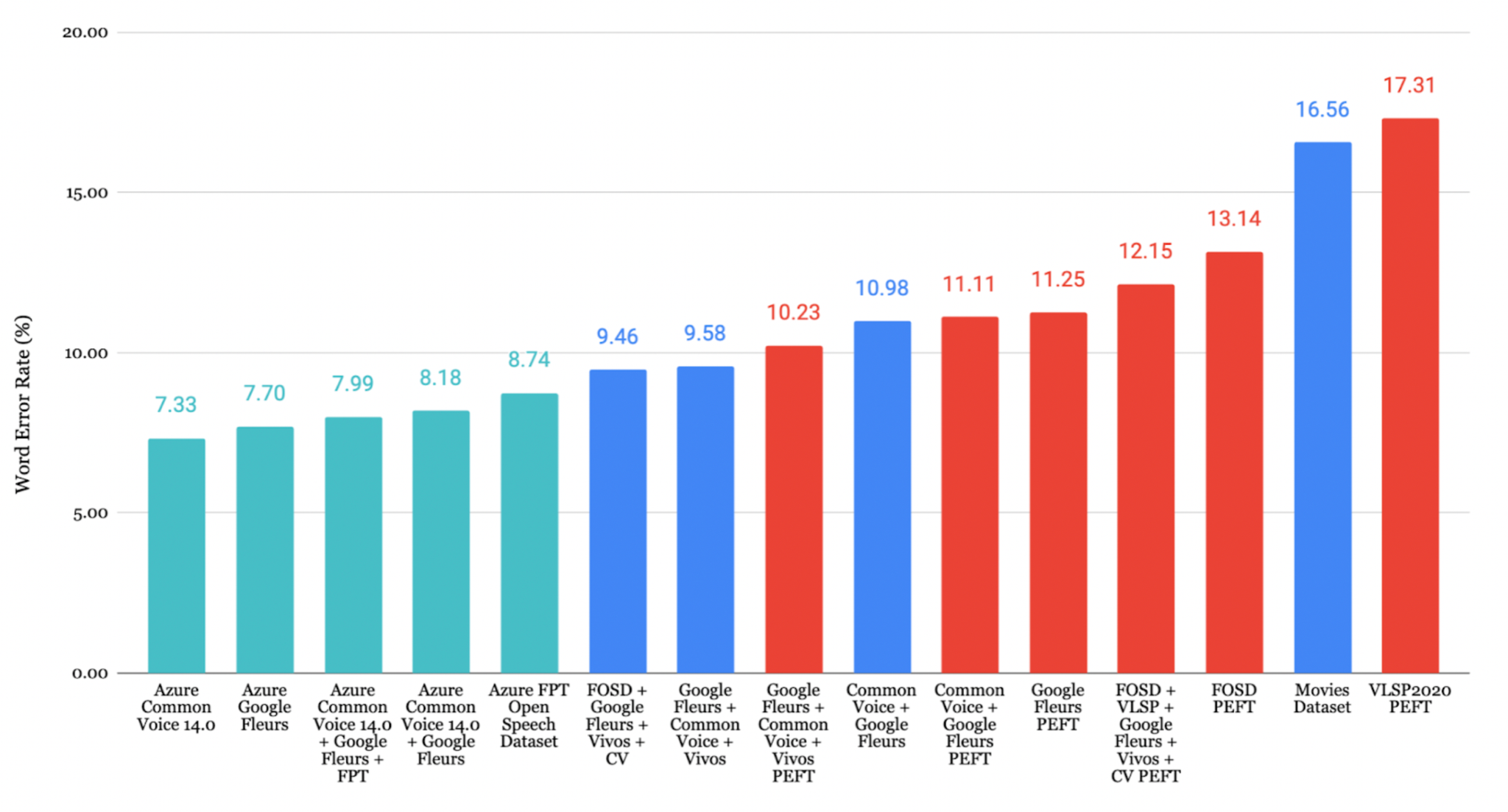
評価対象のデータセットの中で、Google Fleurs + Common Voice + Vivosの組み合わせが最も低いCER 7.84% を記録し、非常に高い書き起こし精度を示しました。
日本語の評価
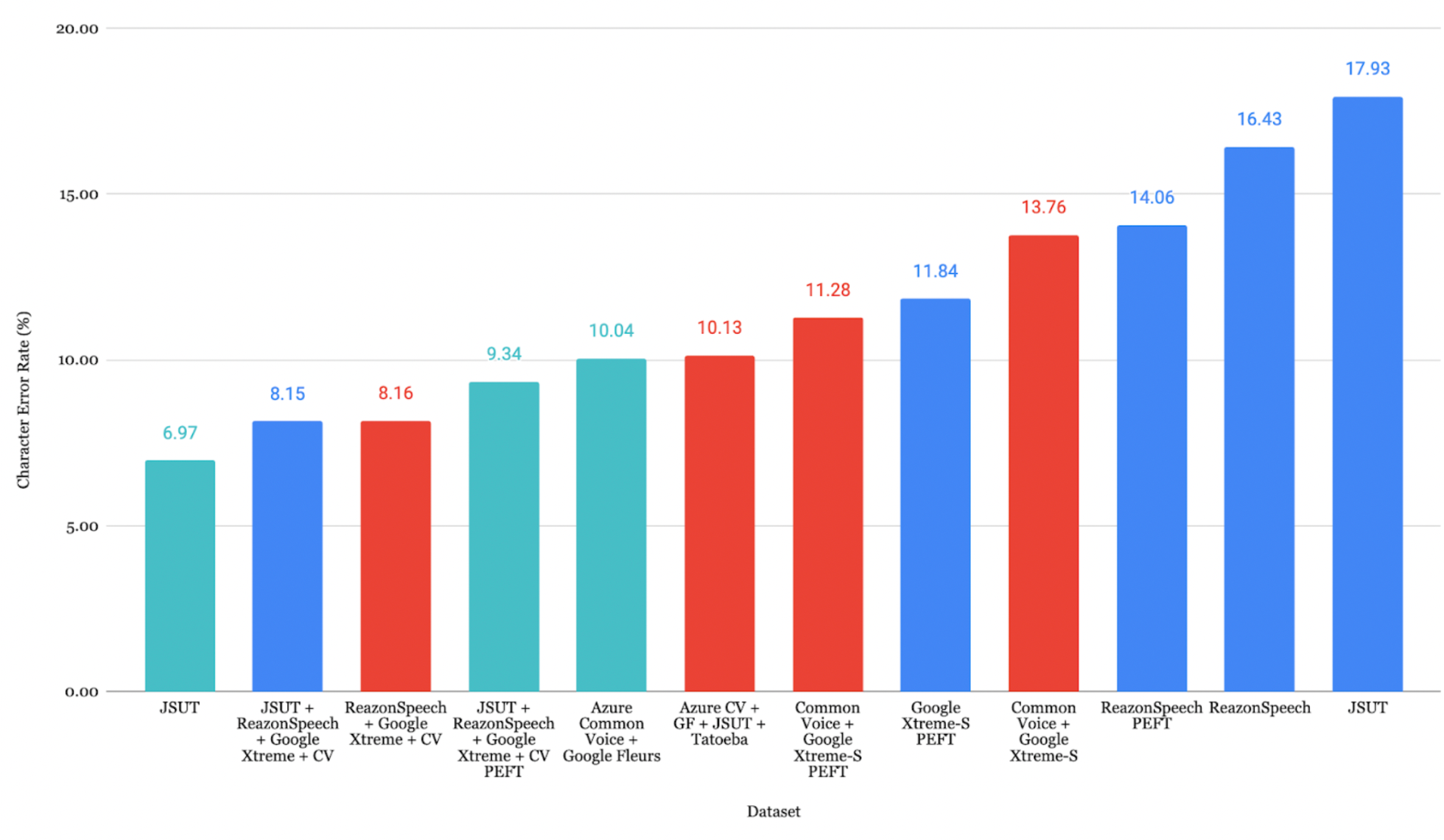
ReazonSpeech + Google Xtreme + CVの組み合わせが最も低いCER 7.44% を達成しました。
Faster-Whisperへの変換
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from ctranslate2.converters import TransformersConverter
model_id = "./whisper-fine-tuned/checkpoint-5000"
output_dir = "whisper-ct2"
converter = TransformersConverter(model_id, load_as_float16=True)
converter.convert(output_dir, quantization="float16")
model = WhisperModel(output_dir, device="cuda", compute_type="float16")
|
注: Faster Whisperは、標準のファインチューニング済みWhisperと同等の精度を維持しながら、推論速度を約40%高速化できます。
9. Azure Speech Studio
Azure Speech Studioは、ASRモデルのファインチューニングに対する代替アプローチを提供します。
Azureによる書き起こし
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import os, evaluate
from azure.cognitiveservices.speech import SpeechConfig, SpeechRecognizer, AudioConfig
subscription_key = "your_subscription_key"
location = "japaneast"
endpoint = "your_endpoint"
config = SpeechConfig(subscription=subscription_key, region=location)
config.endpoint_id = endpoint
speech_config = SpeechConfig(
subscription=subscription_key,
region=location,
speech_recognition_language="ja-JP"
)
predictions = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(wav_base_path):
for file_name in files:
if file_name.endswith(".wav"):
audio_file_path = os.path.join(root, file_name)
audio_config = AudioConfig(filename=audio_file_path)
speech_recognizer = SpeechRecognizer(
speech_config=speech_config,
audio_config=audio_config
)
result = speech_recognizer.recognize_once()
if result.text:
predictions.append(result.text)
|
Azureの結果
ベトナム語: Common Voice 14.0で学習したモデルがWER 7.33% を達成
日本語: JSUTで学習したモデルがCER 6.97% を達成
注意: Azure Speech Studioは学習時のWERが低い場合がありますが、未知のデータ、特に多様で複雑な音声に対しては、Whisperの方が優れた評価結果を示す傾向があります。
10. まとめ
WhisperのASRモデルに対するファインチューニングは、性能を向上させるための有効な手法であることが確認されました。主な知見は以下の通りです。
- DeepLは中国語から英語への翻訳において最も高い精度を示す
- ファインチューニングにより一貫した性能向上が得られる(ベトナム語WER 7.33-12.15%、日本語CER 8.15-17.93%)
- データ拡張はaudiomentationsライブラリによって有効な多様性を導入できる
- データセットの品質が重要: データ量、音声の明瞭さ、トピックの多様性がすべて性能に影響する
- Whisperは実運用環境において、未知のデータに対してAzureよりも優れた性能を発揮する
参考文献
- Radford, A., et al. (2022). Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision. arXiv:2212.04356
- Ardila, R., et al. (2020). Common Voice: A Massively-Multilingual Speech Corpus. arXiv:1912.06670
- Conneau, A., et al. (2022). FLEURS: Few-Shot Learning Evaluation of Universal Representations of Speech. arXiv:2205.12446
- Gandhi, S. (2022). Fine-Tune Whisper for Multilingual ASR with Transformers. Hugging Face Blog
- Mangrulkar, S. & Paul, S. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Using PEFT. Hugging Face Blog