Technical comparison of NeMo MSDD and Pyannote 3.1 across 6 real-world test scenarios
Test Setup: 6 scenarios, 5 languages (EN, JA, KO, VI, ZH), 3 models Hardware: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 Date: December 2025
TL;DR
We evaluated three speaker diarization models across six scenarios:
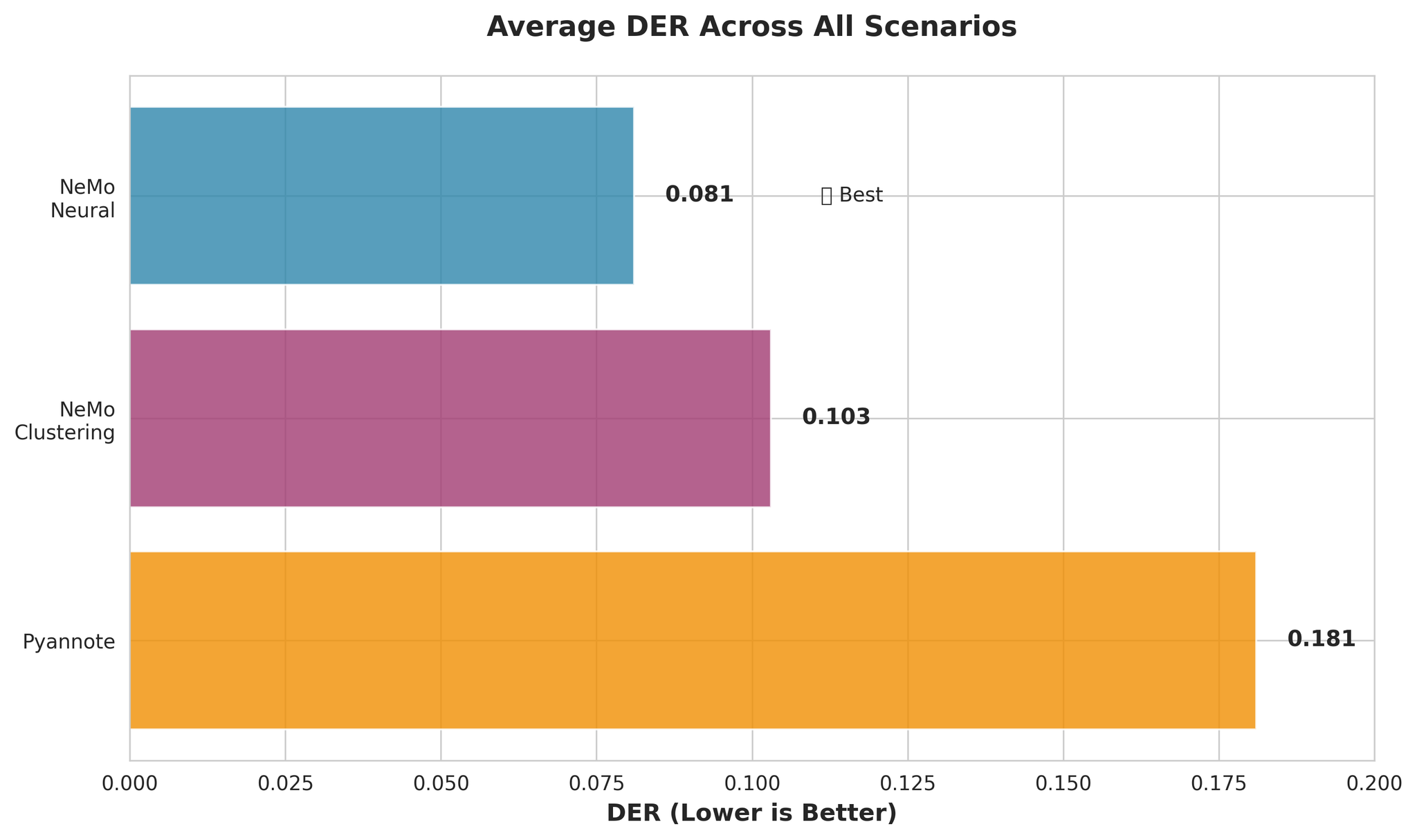
| Model | Description | Avg DER | Avg RTF |
|---|---|---|---|
| NeMo Neural (MSDD) | Multi-Scale Diarization Decoder with neural refinement | 0.081 | 0.020 |
| NeMo Clustering | Clustering-only approach without MSDD | 0.103 | 0.010 |
| Pyannote 3.1 | End-to-end diarization pipeline | 0.181 | 0.027 |
Key Findings:
- NeMo Neural provides best accuracy with fast processing
- Japanese benefits from longer context: Performance improves on 30min+ audio
- Multilingual without Japanese performs excellently (DER: 0.050)
1. Introduction
We needed to choose a diarization model for production. Our evaluation covers 6 scenarios representing real-world conditions:
- Different audio lengths (10 minutes to 1 hour)
- Varying speaker counts (4 to 14 speakers)
- Different overlap levels (0% to 40%)
- Multilingual audio mixing
2. Models Under Test
NeMo Neural (MSDD)
- TitaNet-large for 192-dimensional speaker embeddings
- Processes audio at 5 temporal scales (1.0s-3.0s windows)
- MSDD neural network refines initial clustering results
- Average RTF: ~0.015-0.032
NeMo Clustering (Pure)
- Same embedding model (TitaNet-large)
- Uses only spectral clustering without MSDD refinement
- Significantly faster due to skipping neural refinement
- Average RTF: ~0.014-0.028
Pyannote 3.1
- End-to-end pipeline with VAD, segmentation, and clustering
- Uses pyannote/segmentation-3.0 and wespeaker models
- Average RTF: ~0.018-0.043
3. Evaluation Setup
3.1 Test Scenarios
| Scenario | Duration | Speakers | Overlap | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long Audio | 10min | 4-5 | 15% | Standard production |
| Very Long | 30min | 10-12 | 15% | Stress test |
| 1-Hour Audio | 60min | 12-14 | 15% | Extreme duration |
| High Overlap | 15min | 8-10 | 40% | Worst-case overlap |
| Multilingual (5-lang) | 15min | 8 | 20% | EN+JA+KO+VI+ZH |
| Multilingual (4-lang) | 15min | 8 | 20% | EN+KO+VI+ZH (no JP) |
3.2 Metrics
Accuracy Metrics:
- DER Full (collar=0.0s): Strictest metric, no boundary tolerance
- DER Fair (collar=0.25s): Primary metric with 250ms tolerance
- DER Forgiving (collar=0.25s, overlap ignored): Most lenient
DER Components:
- Miss Rate: Speech missed by the system
- False Alarm Rate: Non-speech marked as speech
- Confusion Rate: Speech assigned to wrong speaker
4. Overall Performance
4.1 Accuracy Comparison

Key Observations:
- NeMo Neural is ~55% more accurate than Pyannote (DER: 0.081 vs 0.181)
- NeMo Clustering performs nearly as well as Neural (only 27% worse)
- Pyannote has 3.4x higher confusion rate
4.2 Speed Comparison
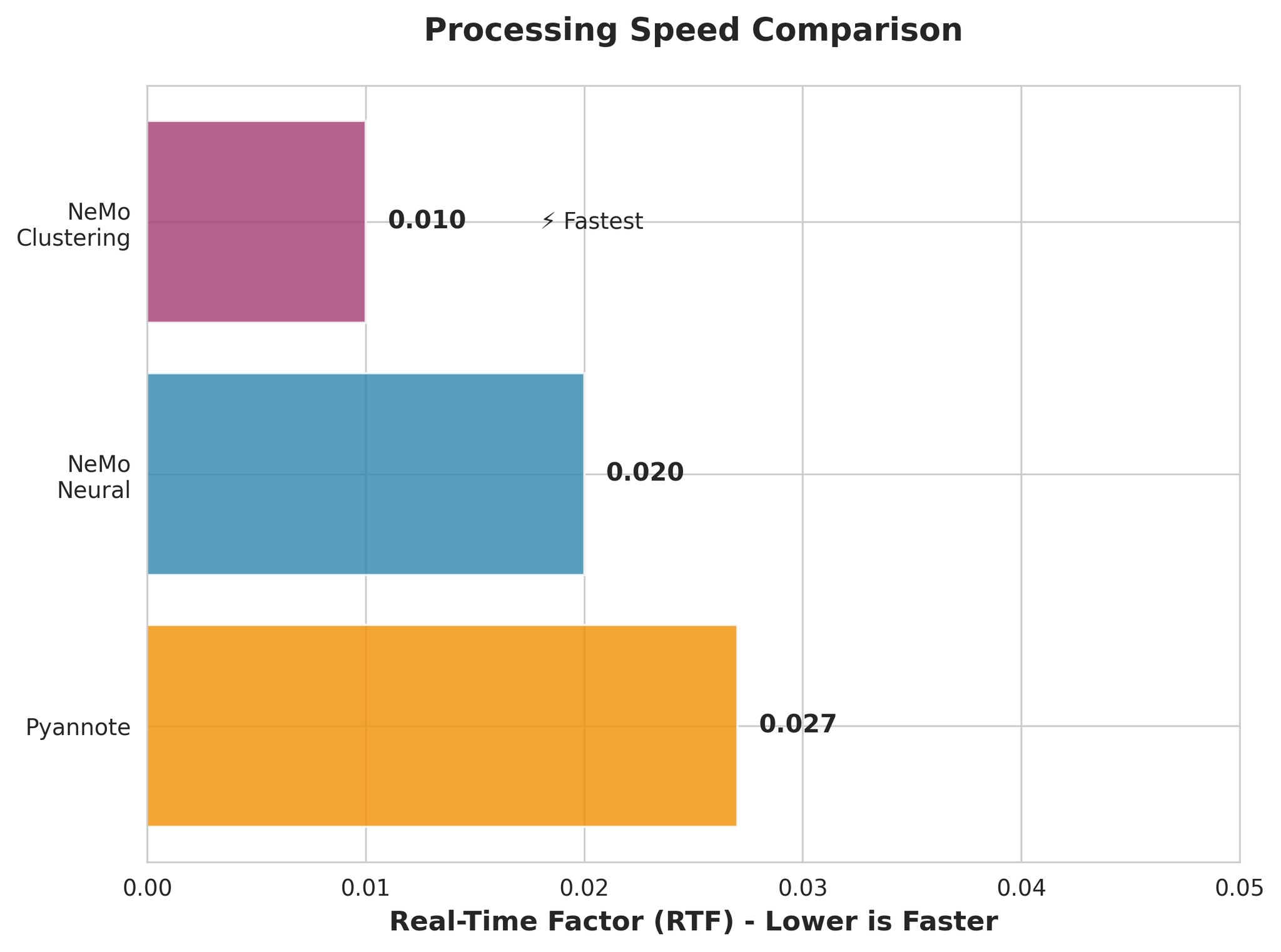
- NeMo Clustering is fastest (RTF 0.010)
- NeMo Neural is very fast (RTF 0.020)
- All models are much faster than real-time
4.3 Accuracy vs Speed Trade-off
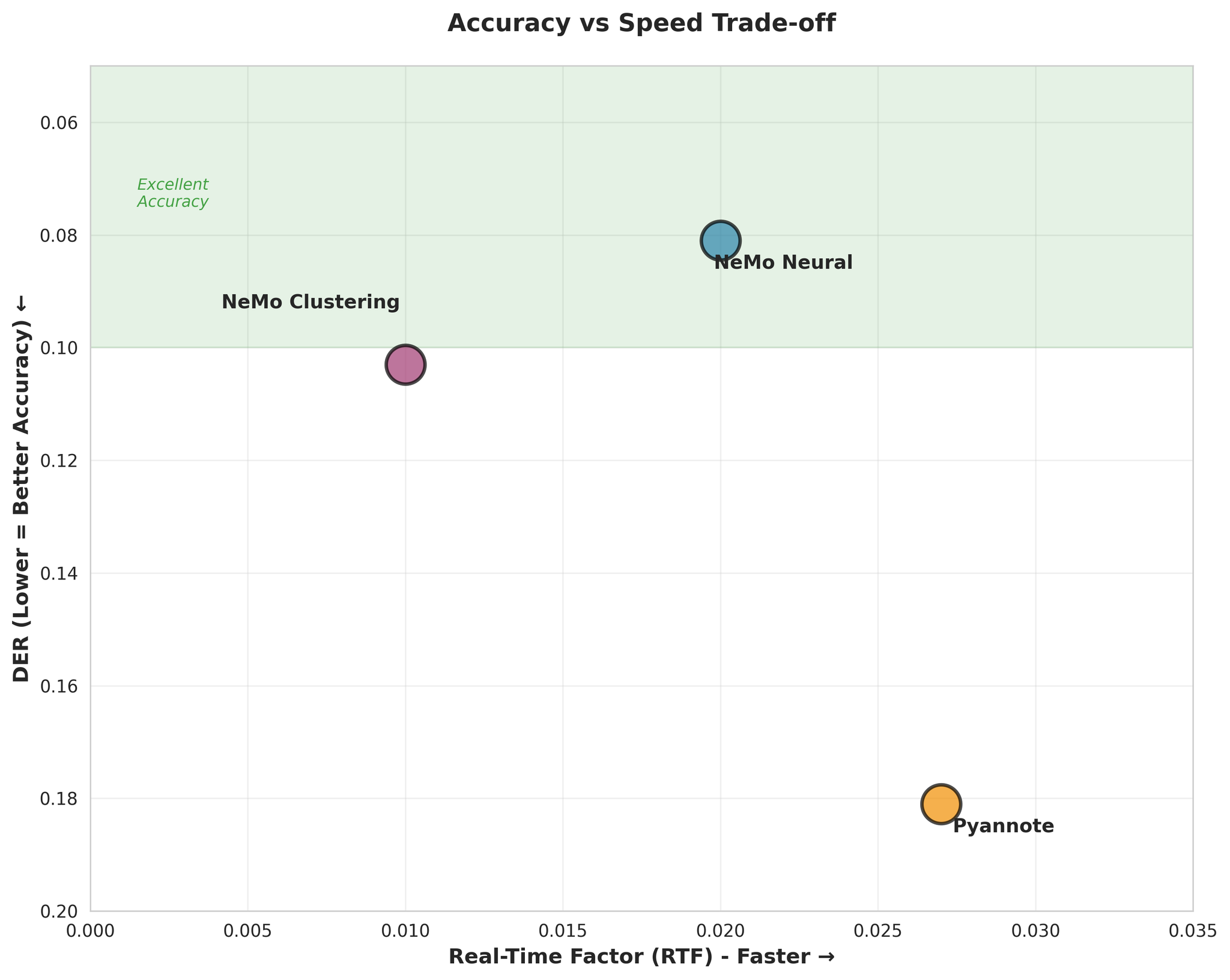
Major Finding: NeMo Neural achieves best accuracy with fast speed, making it the clear winner for most use cases.
5. Results by Scenario
5.1 Long Audio (10 minutes)
NeMo Neural Results by Language:
- EN: 0.019 (Excellent)
- JA: 0.157 (8.3x harder than English)
- KO: 0.046
- VI: 0.037
- ZH: 0.053
- Average: 0.062
5.2 Very Long Audio (30 minutes)
Critical Discovery - Japanese Benefits from Longer Context:
- 10min audio: DER 0.157 (8.3x harder than English)
- 30min audio: DER 0.067 (2.9x harder than English)
Extended duration provides better acoustic context for pitch-accent language modeling.
5.3 High Overlap (40%)
- NeMo Neural and Clustering perform virtually identically (DER: 0.114 vs 0.115)
- Pyannote struggles more (DER: 0.202, ~77% worse than NeMo)
- Japanese remains the hardest language (DER: 0.232)
6. Language-Specific Analysis
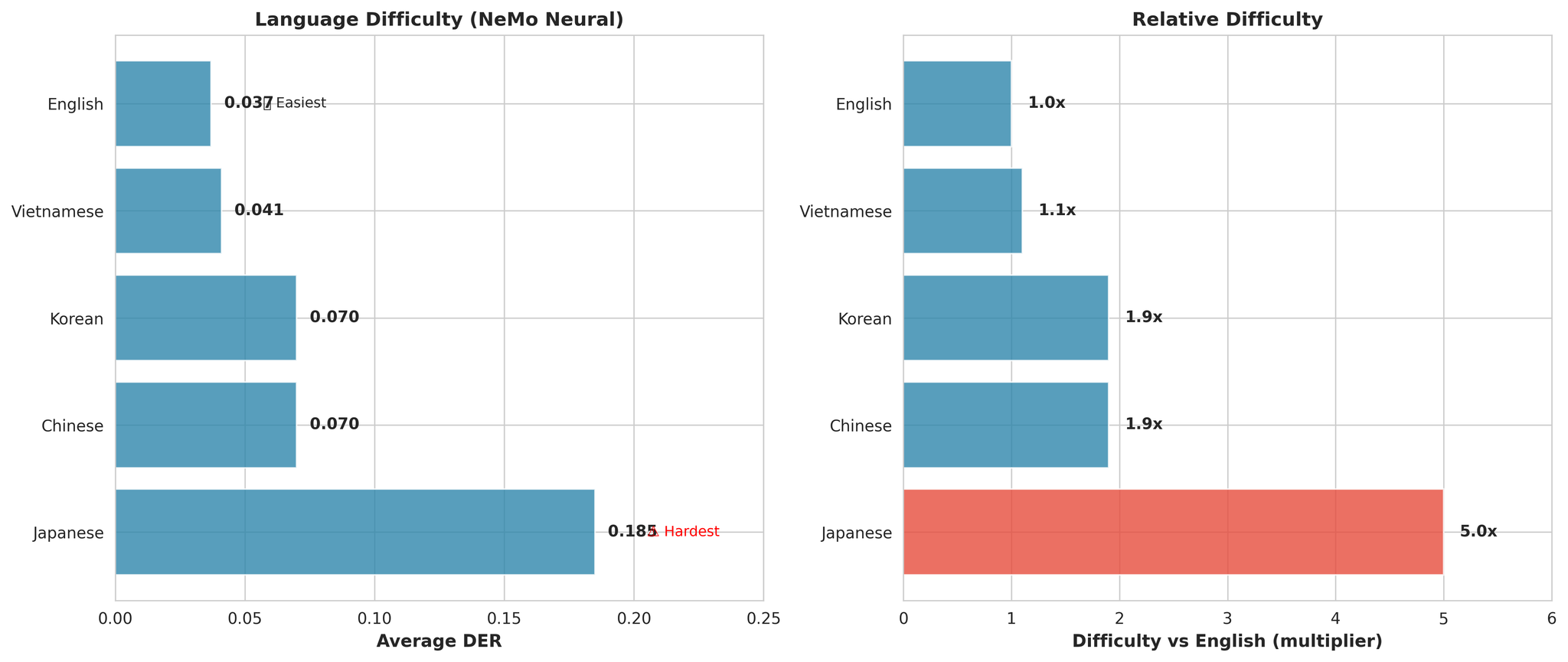
Key Observations:
- Japanese is universally hardest (5.0x harder than English on average)
- English is easiest (DER: 0.037)
- Vietnamese is close second (only 1.1x harder than English)
Why Japanese is Difficult
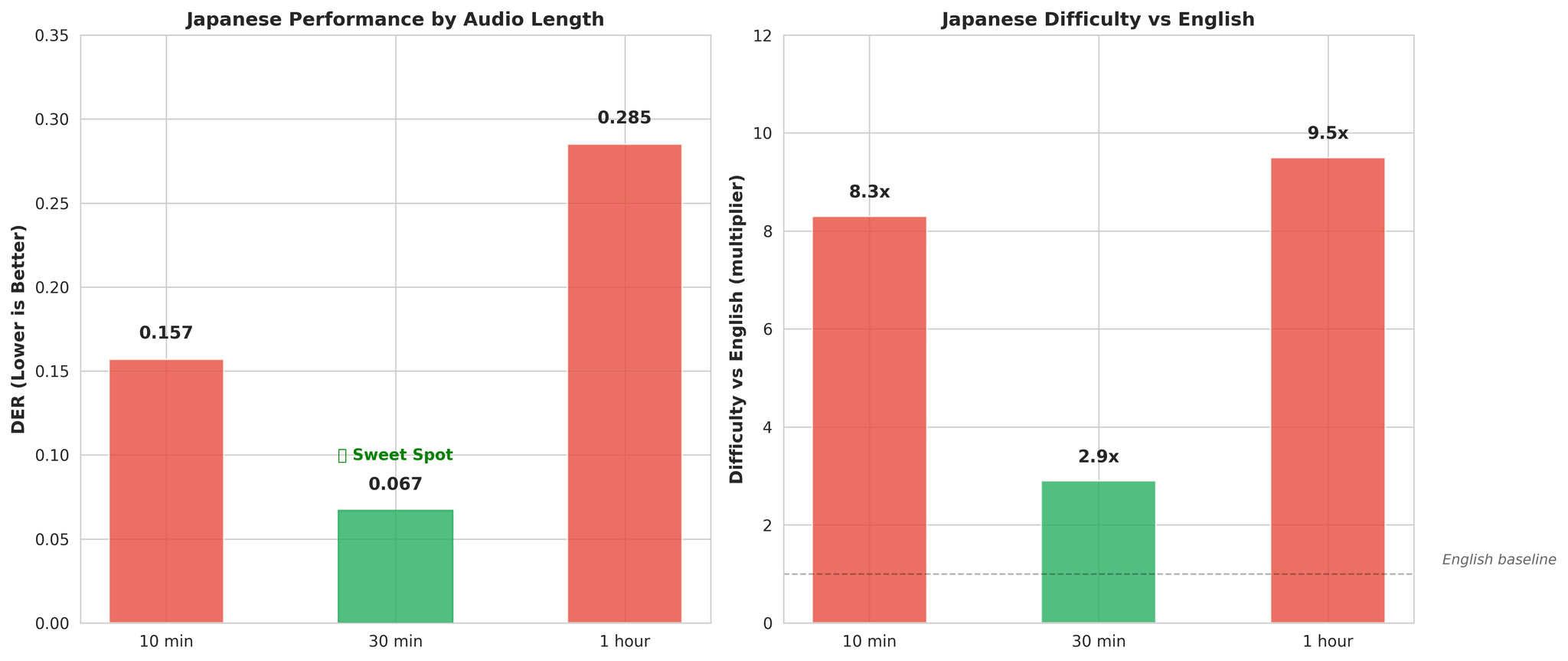
Hypotheses:
- Pitch-accent language: Pitch carries linguistic meaning, confusing speaker embeddings
- Narrow phonetic inventory: ~100 mora vs thousands of English phonemes
- Shorter syllable durations: Less temporal context per speaking turn
7. Neural vs Clustering
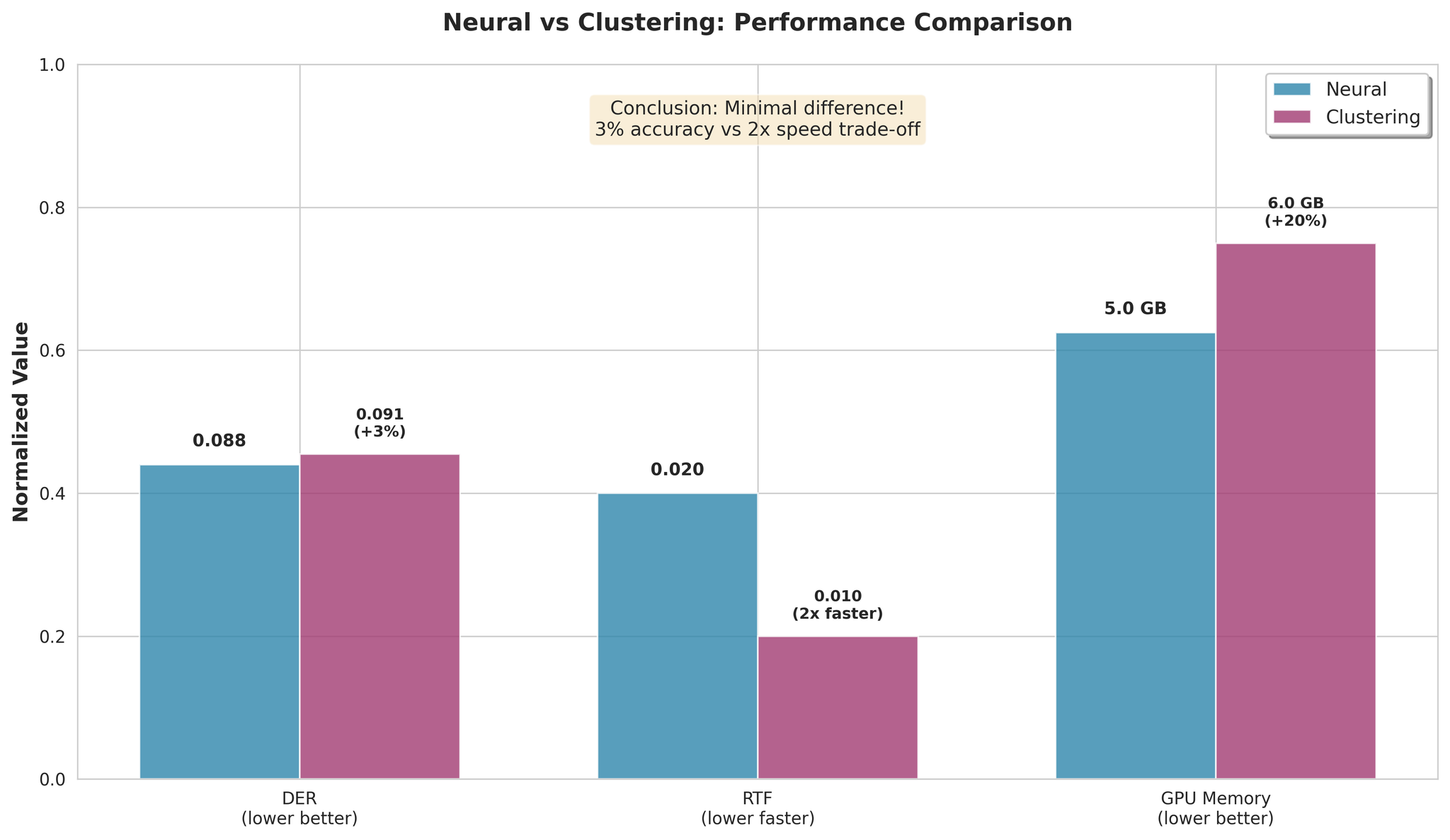
Key Findings:
- Clustering is only 3% worse on average
- Clustering is 2x faster in processing
- The speed/accuracy trade-off is minimal
Recommendation:
- Use NeMo Neural for best accuracy
- Use NeMo Clustering for maximum speed (2x faster, 3% worse)
8. Multilingual Performance
8.1 The Japanese Effect
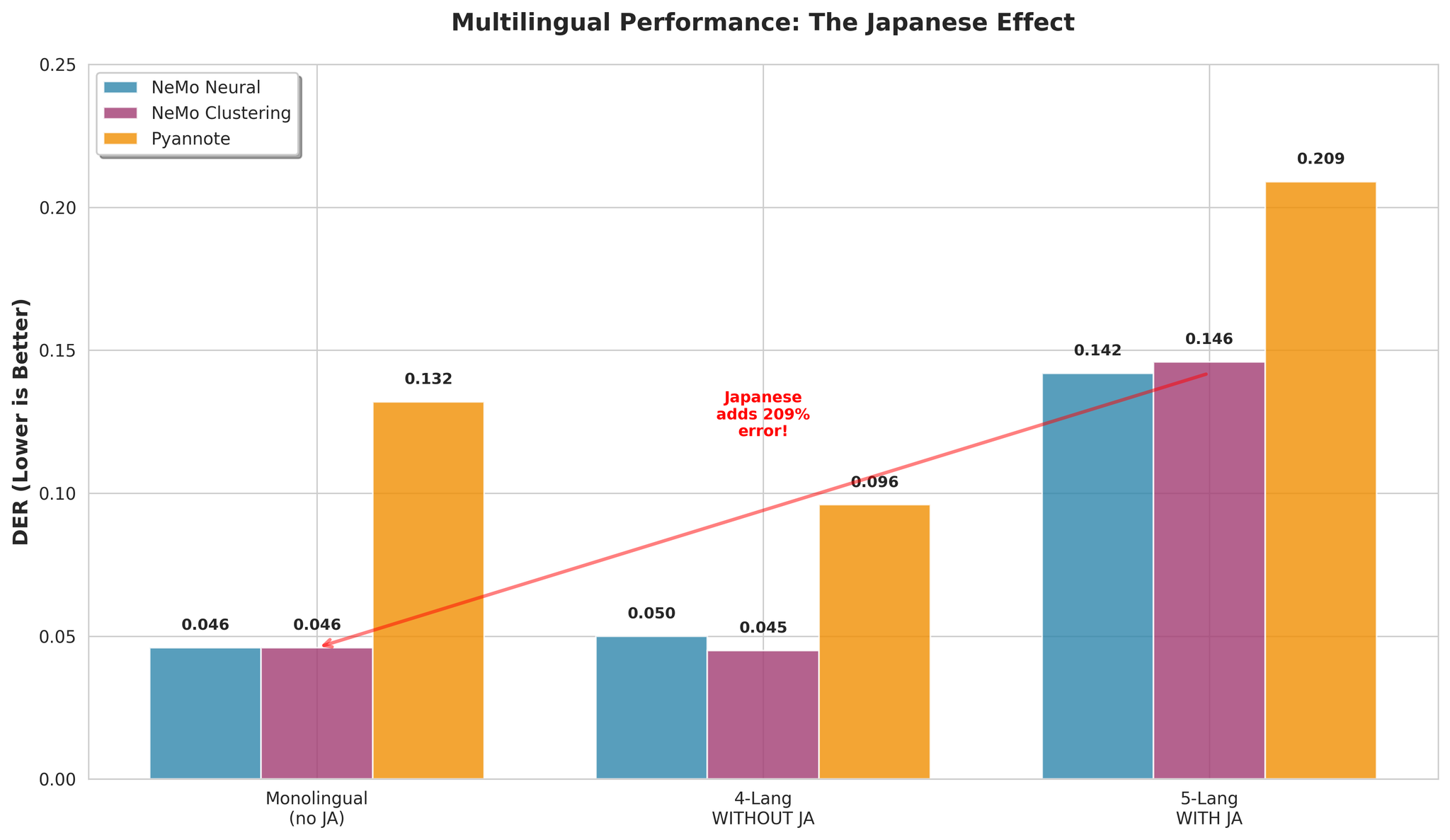
Key Insight: Japanese is the primary factor making multilingual diarization difficult.
| Configuration | NeMo Neural DER |
|---|---|
| With Japanese (5-lang) | 0.142 |
| Without Japanese (4-lang) | 0.050 |
8.2 Error Analysis
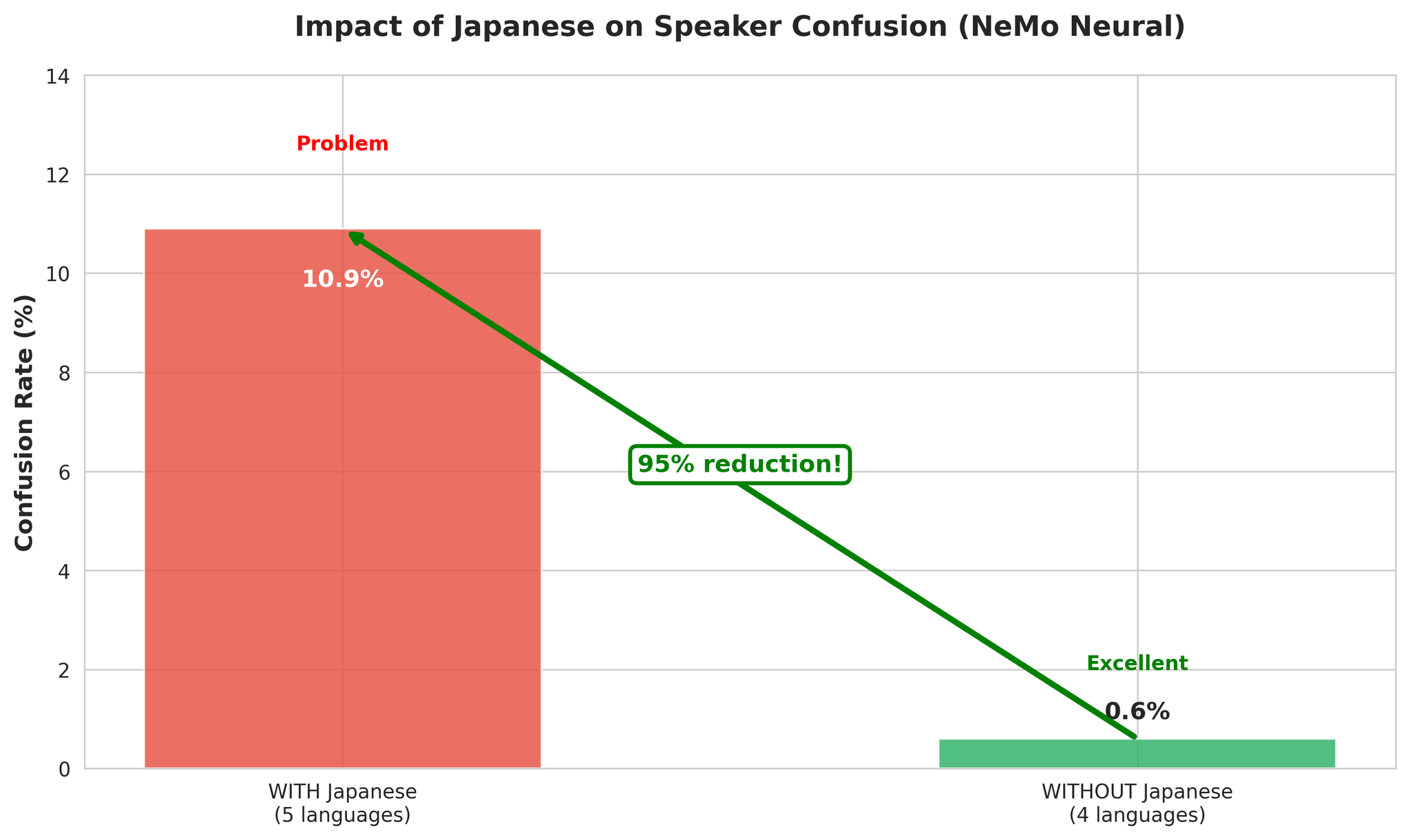
Why 4-Language Multilingual Works Well:
- More acoustic diversity helps VAD detect speech boundaries
- Language changes provide natural segment boundaries
- EN, KO, VI, ZH have compatible acoustic features
- Japanese’s pitch-accent features cause cross-language speaker confusion
9. Conclusion
Key Takeaways
NeMo Neural is the clear winner:
- Best accuracy: DER 0.081 average
- Fast processing: RTF 0.020 (50x faster than real-time)
- Excellent multilingual without Japanese: DER 0.050
Critical Findings:
- Japanese benefits dramatically from longer context (30min optimal)
- Multilingual with Japanese is challenging (DER 0.142) but manageable
- MSDD neural refinement provides minimal benefit over clustering (27% better)
- All models are fast and production-ready
Recommendations
| Use Case | Model | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Best accuracy | NeMo Neural | DER 0.081 |
| Maximum speed | NeMo Clustering | 2x faster |
| Long audio (30min-1h) | NeMo Neural | Handles complexity |
| Multilingual (no Japanese) | NeMo Neural | DER 0.050 |
| Japanese (30min+) | NeMo Neural | Context helps |
Default Choice: NeMo Neural - best accuracy with fast processing.