Research on ASR LLM fine-tuning, speaker diarization, and model comparison
Author: Linchuan Du Affiliation: Department of Mathematics, The University of British Columbia Date: August 2023
Abstract
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), also known as Speech to Text (STT), uses Deep Learning technologies to transcribe speech-included audios to texts. In the fields of Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs) mimic human brains in processing words and phrases, and have the ability to understand and generate text data. LLMs usually contain millions of weights and pre-trained with various kinds of datasets. Specifically, an ASR LLM will convert audio inputs to desired input formats by feature extraction and tokenization.
To customize an ASR LLM with ideal performance, fine-tuning procedures of Whisper, an ASR LLM developed by OpenAI, were tested on Google Colaboratory first. Larger models were then deployed in GPU-equipped environments in Windows OS to speed up training and alleviate GPU availability or limit issues on Colab and MacOS. Audio data were investigated on reliability based on information such as audio quality and transcript accuracy. Models were then improved and optimized by data preprocessing and hyper-parameter tuning techniques. In case of failing to resolve GPU memory issues by means of regular fine-tuning, Parameter-Efficient-Fine-Tuning (PEFT) with Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) was utilized to freeze most parameters to save memory allocation without sacrificing too much in performances. Results were visualized along with loss curves to ensure the fitness and optimization of fine-tuning processes.
Possibility of multi-speaker support in Whisper was explored using Neural Speaker Diarization. Integration with Pyannote was implemented using pipeline and WhisperX, a project containing similar ideas with extra features of word-level timestamps and Voice Activity Detection (VAD). WhisperX was tested on long-form transcription with batching as well as diarization.
Besides Whisper, other models with ASR functionality were installed and compared with Whisper baseline, including Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS) by Meta AI research, PaddleSpeech by PaddlePaddle, SpeechBrain and ESPNet. Chinese datasets were used to compare these models in CER metrics. In addition, Custom Speech in Azure AI, which supports real-time STT features, was introduced to compare performances (mainly Mandarin Chinese). Then a choice can be made between trained Azure models and loadable models like Whisper for deployment.
Overview
Topics covered in this research:
- Preparing Environment - Google Colab, Anaconda, VS Code, CUDA GPU
- Audio Data Source - Hugging Face, OpenSLR datasets
- Whisper Fine-tuning - Fine-tuning, PEFT with LoRA, Results
- Speaker Diarization - Pyannote.audio, WhisperX
- Other Models - Meta MMS, PaddleSpeech, SpeechBrain, ESPnet
- Azure Speech Studio - Custom Speech training and deployment
1. Preparing Environment
a. Google Colaboratory
Google Colaboratory is a hosted Jupyter Notebook service that has limited free GPU & TPU computing resources. In Google Colaboratory, ipynb extension format is used to edit and execute Python scripts.
Log in to Google Colab through Google account, share written scripts with others via “share” on the right top corner of the page, and optionally authorize Colab with a Github account.
How to set up environments on Colab:
- Select Tab Runtime → Change Runtime to enable GPU for use
- Use pip or other package installers to install necessary dependencies
| |
b. Anaconda
Besides Colab, environments can also be prepared on local PCs. Anaconda is a well-known distribution platform for Data Science field, including data analysis and building machine learning models in Python. It contains Conda, an environment and package manager that helps to manage open-source Python packages and libraries.
How to set up environments with Anaconda:
- Install Anaconda from Free Download | Anaconda and add to PATH environment variable
- Search Command Prompt and get into base environment, e.g (Windows):
| |
- Create a new Conda environment with a new name:
| |
- Activate every time a specific Conda environment is needed, or return to base environment using deactivate:
| |
- Install dependencies through PyPI or Conda package manager:
| |
Tip: Other useful Conda commands: https://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/commands
c. Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code, or VS Code, is a powerful source-code editor for Windows, MacOS and Linux with various programming languages available for editing. It supports multiple tasks, including debugging, executing in integrated terminals, enriching functionalities by extensions, and version control by embedded Git.
How to set up environments in VS Code:
- Open the folder(s) on the left side under EXPLORER and create files inside the folder
- On the bottom right, select the environment needed. Execute Python scripts in either interactive window on the top right with IPython kernel installed or executing Python files using commands:
| |
- An alternative way is to use the ipynb extension (Jupyter Notebook)
- The Git icon on the left panel is the place where the source codes are controlled
Tip: VS Code needs to reopen if packages in the environment are updated
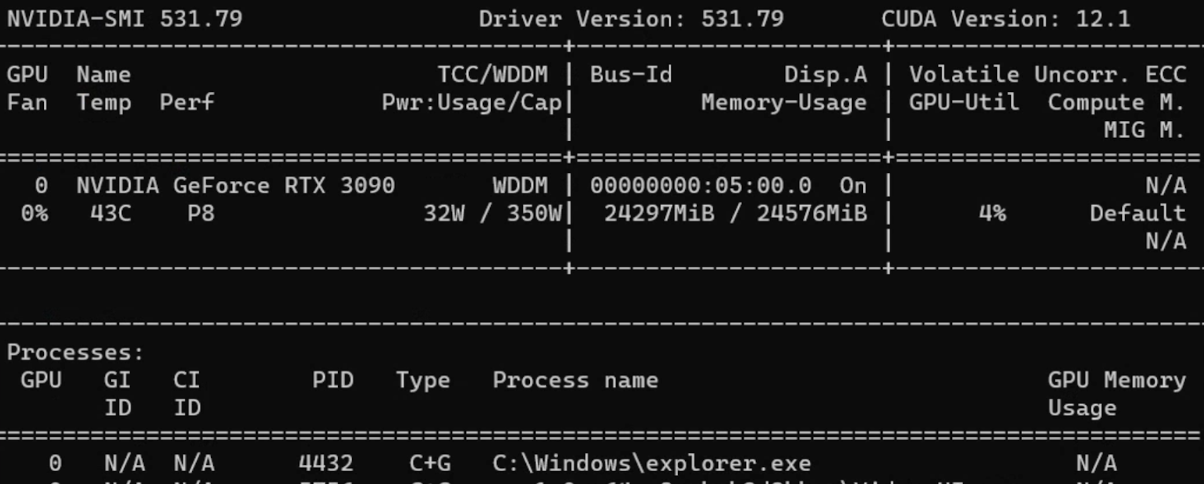
d. CUDA GPU
Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) is a parallel computing platform and Application Programming Interface (API) developed by NVIDIA. It allows developers to use NVIDIA Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) for multiple computing tasks.
How to use CUDA GPU:
- Install the CUDA Toolkit, which includes necessary libraries, tools, and drivers for developing and running CUDA applications
- Check relevant information in Command Prompt with the command:
| |

After setting up CUDA Toolkit, download a GPU-compatible PyTorch version from PyTorch.
Tip: When a previous PyTorch version is needed, check the right commands of Previous PyTorch Versions to avoid compatibility issues.
Version check can be performed directly through Python:
| |
2. Audio Data Source
a. Hugging Face
Hugging Face is a company and an open-source platform dedicated to Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Intelligence.
Create a Hugging Face account to utilize published models or upload customized models. Personal READ and WRITE tokens can be created on https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens.
Common ASR LLMs and their relevant information:
| Model | # Params Size | Languages | Task | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Whisper | large-v2 1550M | Most languages | Multitasks | Transformer encoder-decoder Regularized |
| OpenAI Whisper | large 1550M | Most languages | Multitasks | Transformer encoder-decoder |
| OpenAI Whisper | medium 769M | Most languages | Multitasks | Transformer encoder-decoder |
| OpenAI Whisper | small 244M | Most languages | Multitasks | Transformer encoder-decoder |
| guillaumekln faster-whisper | large-v2 | Most languages | Multitasks | CTranslate2 |
| facebook wav2vec2 | large-960h-lv60-self | English | transcription | Wav2Vec2CTC decoder |
| facebook wav2vec2 | base-960h 94.4M | English | transcription | Wav2Vec2CTC decoder |
| facebook mms | 1b-all 965M | Most languages | Multitasks | Wav2Vec2CTC decoder |
Common audio datasets:
| Dataset | # hours / Size | Languages |
|---|---|---|
| mozilla-foundation common_voice_13_0 | 17689 validated hrs | 108 languages |
| google fleurs | ~12 hrs per language | 102 languages |
| LIUM tedlium | 118 to 452 hrs for 3 releases | English |
| librispeech_asr | ~1000 hrs | English |
| speechcolab gigaspeech | 10000 hrs | English |
| PolyAI minds14 | 8.17k rows | 14 languages |
Warning: PolyAI/minds14 is primarily for intent detection task, and not ideal for ASR purpose
b. Open SLR
Open SLR is another useful website that hosts speech and language resources with compressed files. Various audio datasets can be seen along with their brief summaries in the Resources tab.
Chinese audio datasets for ASR purposes:
| Dataset | # hours (size) | # speakers | Transcript accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aishell-1 (SLR33) | 178 hrs | 400 | 95+% |
| Free ST (SLR38) | 100+ hrs | 855 | / |
| aidatatang_200zh (SLR62) | 200 hrs | 600 | 98+% |
| MAGICDATA (SLR68) | 755 hrs | 1080 | 98+% |
3. Whisper Model Fine-tuning
Whisper is an ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) system released by OpenAI in September, 2022. It was trained on 680,000 hours of multilingual and multitask supervised data, enabling multiple language transcription and translation. The architecture is an encoder-decoder Transformer.
The audios will be chunked into 30 seconds and converted into a log-Mel spectrogram, which enables frequencies to be changed into the Mel scale. Then it will be passed into an encoder.
Resources:
a. Fine-tuning on Colab
Step 1: Login through Hugging Face token to enable datasets download
| |
Step 2: Load desired dataset(s) through load_dataset in datasets
Tip: Sometimes permissions for access to certain datasets are needed on Hugging Face
Step 3: Preprocess datasets to feed data into Whisper:
- Manipulate columns: e.g.
remove_columns,cast_column - Normalize transcript, e.g. upper/lowercase, punctuations, special tokens
- Change sampling rate to 16k using Audio in Datasets library
- Load pre-trained feature extractor and tokenizer from transformers library
| |
Tip: AutoProcessor detects processor type automatically
In tokenizer, usually target languages and tasks are specified:
| |
Step 4: Define Data Collator in Sequence to Sequence with label padding
| |
Step 5: Import evaluation metrics (WER)
| |
Tip: When using English or most European languages, WER (Word Error Rate) is a common evaluation metric for transcription accuracy.
WER Formula: WER = (Substitutions + Deletions + Insertions) / Total Words in Reference
Step 6: Design metrics computation
| |
Step 7: Load conditional generation and configure model
| |
Step 8: Define hyperparameters in Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
| |
Step 9: Start training with trainer.train()
| |
Handling CUDA Out of Memory (OOM) Errors:
- First priority: Reduce batch size to use more time to compensate for memory savings. Work along with gradient accumulation.
- Gradient checkpointing: Trades a small increase in computation time for significant reductions in memory usage.
- Mixed precision training: Reduces memory footprint significantly while maintaining training stability.
- Clear GPU cache:
| |
Tip: If all methods fail, changing to a smaller model size can be the last resort. Less model complexity will help save GPU memories.
b. Data Preprocessing
Hugging Face Dataset
Load the dataset using the load_dataset function:
| |
Tip: Use “streaming=True” when space is limited on the disk, or if the download of the whole dataset is unnecessary.
Change sampling rate to 16k Hz (required by Whisper architecture):
| |
Transcript Cleaning
| |
| |
c. Fine-tuned Results
Abbreviations:
- lr = learning rate, wd = weight decay, ws = warmup steps
- ms = max steps, #e = number of epochs
- es = evaluation strategy, ml = max length
- tbz = train batch size, ebz = eval batch size
- #ts = train sample size, #es = eval sample size
| Dataset/Size/Split | Model/Lang/Task | Hyperparameters | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| common_voice_11_0 #ts=100, #es=100 train/test | Whisper small Hindi Transcribe | lr=1e-5, wd=0, ws=5, ms=40, es=steps, ml=225, tbz=4, ebz=8 | WER: 67.442% |
| common_voice_11_0 #ts=500, #es=500 train+validation/test | Whisper small Hindi Transcribe | lr=1e-5, wd=0, ws=0, ms=60, es=steps, ml=50, tbz=16, ebz=8 | WER: 62.207% |
| common_voice #ts=3500, #es=500 train+validated/validation | Whisper small Japanese Transcribe | lr=1e-6, wd=0, ws=50, ms=3500, es=steps, ml=200, tbz=16, ebz=8 | WER: 2.4% |
| librispeech_asr #ts=750, #es=250 train.100/validation | Whisper medium English Transcribe | lr=1e-5, wd=0.01, ws=10, ms=750, es=steps, ml=80, tbz=1, ebz=1 | WER: 13.095% |
Note: As Japanese is character-based, a more suitable evaluation metric is Character Error Rate (CER).
d. PEFT with LoRA
Parameter-Efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT) approaches only fine-tune a small number of model parameters while freezing most parameters of the pre-trained LLMs, greatly decreasing computational and storage costs.
LoRA (Low Rank Adaptation) decomposes the weights of pre-trained models into low-rank matrices or tensors and significantly reduces the number of parameters that need to be fine-tuned.
| |
PEFT Training Arguments:
| |
PEFT Results:
| Dataset/Size/Split | Model/Lang/Task | Hyperparameters | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| common_voice_13_0 #ts=1000, #es=100 train+validation/test | Whisper medium Japanese Transcribe | lr=1e-3, wd=0, ws=50, #e=3, es=steps, ml=128, tbz=8, ebz=8 | WER: 73%, NormWER: 70.186% |
| common_voice_13_0 #ts=100, #es=30 train+validation/test | Whisper large-v2 Vietnamese Transcribe | lr=1e-4, wd=0.01, ws=0, #e=3, es=steps, ml=150, tbz=8, ebz=8 | WER: 26.577%, NormWER: 22.523% |
Tip: Resources for PEFT:
e. Loss Curves Visualization
| |
Key patterns to identify:
- Overfitting: Low training loss but high validation loss
- Underfitting: High training and validation loss
- Smoothness: Smooth curves indicate well-behaved training
- Loss Plateau: Model struggles to learn further from available data
f. Baseline Results
| Dataset/Split/Size | Model/Task | Result |
|---|---|---|
| distil-whisper/tedlium-long-form test | Whisper medium baseline en→en | WER: 28.418% |
| distil-whisper/tedlium-long-form validation | Whisper large-v2 baseline en→en | WER: 26.671% |
| librispeech_asr clean test | Whisper large-v2 baseline en→en | WER: 4.746% |
| Aishell S0770 test #353 | Whisper large-v2 baseline zh-CN→zh-CN | CER: 8.595% |
| Aishell S0768 test #367 | Whisper large-v2 baseline zh-CN→zh-CN | CER: 12.379% |
| MagicData 38_5837 test #585 | Whisper large-v2 baseline zh-CN→zh-CN | CER: 21.750% |
4. Speaker Diarization
Speaker Diarization involves segmenting speech audio into distinct segments corresponding to different speakers. The goal is to identify and differentiate individual speakers in an audio stream.
a. Pyannote.audio
Pyannote-audio is an open-source toolkit for speaker diarization, voice activity detection, and speech turn segmentation.
How to use Pyannote.audio with Whisper:
| |
| |
| |
b. WhisperX
WhisperX integrates Whisper, Phoneme-Based Model (Wav2Vec2) and Pyannote.audio. It claims to be 70x faster in real-time speech recognition than Whisper large-v2 with word-level timestamps and speaker diarization with VAD feature.
| |
| |
Tip: Advantages:
- WhisperX: Multi-speaker scenario, VAD, Extra Phoneme model, Easier for local audios
- Whisper Pipeline: More languages, Flexible chunk length (≤30s), Easier for HF datasets
WhisperX Results:
| Dataset | Model/Task/Compute Type | Result |
|---|---|---|
| TED LIUM 1st release SLR7 test | WhisperX medium en→en int8 | WER: 37.041% |
| TED LIUM 1st release SLR7 test | WhisperX large-v2 en→en int8 | WER: 36.917% |
| distil-whisper/tedlium-long-form validation | WhisperX large-v2 en→en int8 batch_size=1 | WER: 24.651% |
| distil-whisper/tedlium-long-form validation | WhisperX medium en→en int8 batch_size=1 | WER: 24.353% |
| AISHELL-4 selected audio file | WhisperX manual check | CER: 15.6%~24.658% |
5. Other Models
a. Meta MMS
The Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS) project by Meta expands speech technology from around 100 languages to more than 1,100 languages.
| |
b. PaddleSpeech
PaddleSpeech is a Chinese open-source toolkit on the PaddlePaddle platform. Available architectures include DeepSpeech2, Conformer, and U2 (Unified Streaming and Non-streaming). See the feature list for details.
| |
| |
Tip: ASR training tutorial on Linux: asr1
c. SpeechBrain
SpeechBrain is an open-source conversational AI toolkit developed by the University of Montreal.
| |
| |
d. ESPnet
ESPnet is an end-to-end speech processing toolkit covering speech recognition, text-to-speech, speech translation, and speaker diarization.
| |
| |
e. Baseline Results Comparison
English:
| Dataset | Model/Method | WER |
|---|---|---|
| librispeech_asr clean | Meta MMS mms-1b-all | 4.331% |
| common_voice_13_0 #1000 | Meta MMS mms-1b-all | 23.963% |
Chinese:
| Dataset | Model/Method | CER |
|---|---|---|
| Aishell S0770 #353 | PaddleSpeech Default (conformer_u2pp_online_wenetspeech) | 4.062% |
| Aishell S0768 #367 | SpeechBrain wav2vec2-transformer-aishell | 8.436% |
| Aishell S0768 #367 | Meta MMS mms-1b-all | 34.241% |
| MagicData 4 speakers #2372 | PaddleSpeech conformer-wenetspeech | 9.79% |
| MagicData 4 speakers #2372 | SpeechBrain wav2vec2-ctc-aishell | 15.911% |
| MagicData 4 speakers #2372 | Whisper large-v2 baseline | 24.747% |
Key Finding: For Chinese inference, PaddleSpeech had better performance compared to Whisper, while Meta MMS Chinese transcription results were worse than Whisper.
6. Azure Speech Studio
Azure AI Speech Services is a collection of cloud-based speech-related services offered by Microsoft Azure. Custom Speech Projects in Speech Studio can be created in different languages.
a. Upload Datasets
Three methods for uploading training and testing datasets:
- Speech Studio (direct upload)
- REST API
- CLI usage
Azure Blob Storage:
| |
Audio format requirements:
- Format: WAV
- Sampling rate: 8k Hz or 16k Hz
- Channels: Single channel (mono)
- Archive: ZIP format, under 2GB and 10k files within
b. Train and Deploy Models
| |
c. Azure Results
| Test Dataset | Train Datasets | Error Rate (Custom vs Baseline) |
|---|---|---|
| MagicData 9452 11:27:39s | Aishell 12+ hrs | 4.69% / 4.24% |
| MagicData 9452 11:27:39s | Aishell+Minds14 32+ hrs: 1+ hr | 4.67% / 4.23% |
| MagicData+Aishell+CV13 8721 11:45:52s | Aishell+CV13 8+ hrs: 7+ hrs | 2.51% / 3.70% |
| MagicData+Aishell+CV13 8721 11:45:52s | Aishell+CV13+Fleurs 8+ hrs: 7+ hrs: 9+ hrs | 2.48% / 3.70% |
Note: The best Azure model was trained with AISHELL-1, mozilla-foundation/common_voice_13_0 and google/fleurs, resulting in 2.48% error rate.
7. Prospect
Key findings and future directions:
Data sources: Chinese sources with high transcript quality are much less available than English sources.
Hardware limitations: Multi-GPU training or more advanced GPUs (NVIDIA 40 series) could help achieve better results with larger models.
LoRA configurations: Effects of different LoRA parameters on PEFT model performance could be explored further.
Speaker Diarization: While Pyannote.audio with Whisper integration shows potential, current diarizing ability in multi-speaker meeting scenarios is still not sufficient.
Azure Speech Services: Keep good audio qualities and word-level accuracy in transcripts. Filtering training audio files that are not in good quality can enhance model performances.
8. References
- Anaconda, Inc. (2017). Command reference - conda documentation. conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/commands
- OpenAI (2022, September 21). Introducing Whisper. openai.com/research/whisper
- Radford, A., Kim, J.W., Xu, T., Brockman, G., McLeavey, C., & Sutskever, I. (2022). Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision.
- Gandhi, S. (2022, November 3). Fine-Tune Whisper for Multilingual ASR with Transformers. huggingface.co/blog/fine-tune-whisper
- The Linux Foundation (2023). Previous PyTorch Versions. pytorch.org/get-started/previous-versions
- Hugging Face, Inc. (2023). Hugging Face Documentations. huggingface.co/docs
- Srivastav, V. (2023). fast-whisper-finetuning. github.com/Vaibhavs10/fast-whisper-finetuning
- Mangrulkar, S., & Paul, S. (2023). Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Using PEFT. huggingface.co/blog/peft
- Bredin, H., et al. (2020). pyannote.audio: neural building blocks for speaker diarization. ICASSP 2020.
- Bain, M., Huh, J., Han, T., & Zisserman, A. (2023). WhisperX: Time-Accurate Speech Transcription of Long-Form Audio. INTERSPEECH 2023.
- Meta AI (2023, May 22). Introducing speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and more for 1,100+ languages. ai.meta.com/blog/multilingual-model-speech-recognition
- Pratap, V., et al. (2023). Scaling Speech Technology to 1,000+ Languages. arXiv.
- Zhang, H. L. (2022). PaddleSpeech: An Easy-to-Use All-in-One Speech Toolkit. NAACL 2022.
- Ravanelli, M., et al. (2021). SpeechBrain: A General-Purpose Speech Toolkit.
- Gao, D., et al. (2022). EURO: ESPnet Unsupervised ASR Open-source Toolkit. arXiv:2211.17196.
- ESPnet (2021). espnet_model_zoo. github.com/espnet/espnet_model_zoo
- Microsoft (2023). Custom Speech overview - Azure AI Services. learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/speech-service/custom-speech-overview
- Microsoft (2023). Speech service documentation. learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/speech-service/